Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- presencia de factores de riesgo
- fiebre
- tos productiva
- ruidos respiratorios cavernosos (anfóricos)
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- soplo cardíaco
- dolor torácico pleurítico
- síntomas constitucionales
- caquexia
- palidez
- enfermedad gingival
- halitosis
- ausencia del reflejo faríngeo
- disnea
- hemoptisis
- escalofríos intensos
- debilidad
- artralgia
- lesiones hemorrágicas
- crepitantes inspiratorios
- respiración bronquial
- ruidos respiratorios reducidos
- roncus fijo unilateral
Fatores de risco
- predisposición a la aspiración de contenido gástrico
- higiene dental deficiente y extracción de piezas dentales
- obstrucción bronquial
- inmunosupresión
- enfermedad crónica
- sepsis extrapulmonar
- neumonía
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- hemograma completo (HC)
- radiografía de tórax
- tinción de Gram del esputo
- cultivo de esputo
- hemocultivo
- cultivo del líquido de empiema
Investigações a serem consideradas
- tomografía computarizada (CT) de tórax
- broncoscopia
- cultivos cuantitativos de muestras tomadas con cepillo protegido
- cultivos cuantitativos de muestras de lavado broncoalveolar protegido
- aspiración con aguja percutánea y cultivo
- citología de esputo
- ultrasonido de pulmón
- ecocardiograma
- ensayo inmunoenzimático rápido (ELISA) para el dímero D
- tomografía computarizada de tórax con detector múltiple
- gammagrafía de ventilación-perfusión
Algoritmo de tratamento
probabilidad baja de microorganismos gramnegativos o resistentes a múltiples fármacos
probabilidad alta de microorganismos gramnegativos o resistentes a múltiples fármacos
probabilidad baja de microorganismos gramnegativos o resistentes a múltiples fármacos
alta probabilidad de microorganismos gramnegativos o resistentes a múltiples fármacos: con o sin alergia a penicilina/cefalosporina
Colaboradores
Autores
Ioannis P. Kioumis, MD, PhD

Professor of Respiratory Medicine and Infectious Diseases
Aristotle University of Thessaloniki
Respiratory Failure Clinic
General Hospital G. Papanikolaou
Thessaloniki
Greece
Declarações
IPK declares that he has no competing interests.
Georgia G. Pitsiou, MD, PhD

Professor of Respiratory Medicine
Aristotle University of Thessaloniki
Respiratory Failure Clinic
General Hospital G. Papanikolaou
Thessaloniki
Greece
Declarações
GGP declares that she has no competing interests.
Revisores
William G. Cheadle, MD
Professor of Surgery
University of Louisville
Associate Chief of Staff for Research and Development
VAMC Louisville
Louisville
KY
Declarações
WGC declares that he has no competing interests.
Nicholas Maskell, MD
Senior Lecturer and Consultant Physician
North Bristol Lung Centre
Southmead Hospital
Bristol
UK
Declarações
NM declares that he has no competing interests.
Najib Rahman, BM, BCh, MA (Oxon), MRCP (UK)
MRC Training Fellow and Specialist Registrar, Respiratory Medicine
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine
Churchill Hospital
Oxford
UK
Declarações
NR declares that he has no competing interests.
Philip W. Ind, BA (Cantab), MB BChir, MA (Cantab), FRCP
Consultant Physician
Honorary Senior Lecturer
Imperial College Healthcare Trust
Hammersmith Hospital
London
UK
Divulgaciones
PWI declares that he has no competing interests.
Agradecimiento de los revisores por pares
Los temas de BMJ Best Practice se actualizan de forma continua de acuerdo con los desarrollos en la evidencia y en las guías. Los revisores por pares listados aquí han revisado el contenido al menos una vez durante la historia del tema.
Divulgaciones
Las afiliaciones y divulgaciones de los revisores por pares se refieren al momento de la revisión.
Referencias
Artículos principales
Walters J, Foley N, Molyneux M. Continuing education in anaesthesia, critical care and pain: pus in the thorax: management of empyema and lung abscess. 2011 Dec 1;11(6):229-33.Texto completo
American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: radiologic management of infected fluid collections. 2019 [internet publication].Texto completo
American College of Radiology; Society of Interventional Radiology; Society for Pediatric Radiology. ACR-SIR-SPR practice guideline for specifications and performance of image-guided percutaneous drainage/aspiration of abscesses and fluid collections (PDAFC). 2023 [internet publication].Texto completo
Artículos de referencia
Una lista completa de las fuentes a las que se hace referencia en este tema está disponible para los usuarios con acceso a todo BMJ Best Practice.
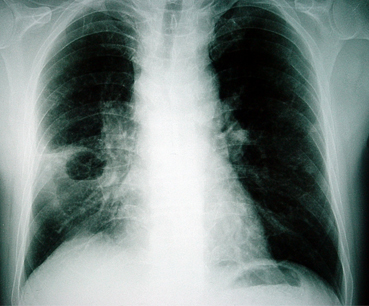
Diferenciales
- Neoplasia (cáncer de pulmón primario o metastásico, linfoma)
- Tuberculosis
- Neumonía necrosante
Más DiferencialesGuías de práctica clínica
- Practice guideline for specifications and performance of image-guided percutaneous drainage/aspiration of abscesses and fluid collections (PDAFC)
- Appropriateness criteria: radiologic management of infected fluid collections
Más Guías de práctica clínicaInicie sesión o suscríbase para acceder a todo el BMJ Best Practice
El uso de este contenido está sujeto a nuestra cláusula de exención de responsabilidad