Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presencia de factores de riesgo
- disuria (en mujeres)
- linfadenopatía
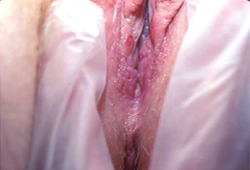
- úlcera genital
- úlcera oral
- fiebre
Other diagnostic factors
- sensación de hormigueo
- cefalea/meningitis aséptica
Risk factors
- infección por VIH (factor de riesgo para enfermedad clínica)
- uso de medicamentos inmunosupresores (factor de riesgo para enfermedad clínica)
- sexo femenino (factor de riesgo para seropositividad)
- raza negra (factor de riesgo para seropositividad)
- aumenta con la edad (factor de riesgo para seropositividad)
- comportamiento sexual de alto riesgo (factor de riesgo para seropositividad)
- no usar condones (factor de riesgo para seropositividad)
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- reacción en cadena de la polimerasa del VHS (PCR)
- cultivo viral
Tests to consider
- serología específica de tipo basada en glucoproteína G (gG1 y gG2)
Treatment algorithm
Afectación del SNC: encefalitis o meningitis
afectación visceral diseminada: esofagitis, neumonitis o hepatitis
enfermedad genital: primer episodio, inmunocompetente, no embarazada
enfermedad genital: primer episodio, inmunocomprometida, no embarazada
enfermedad genital: episodio recurrente, inmunocompetente, no embarazada
enfermedad genital: episodio recurrente, inmunocomprometida, no embarazada
enfermedad genital: episodio primario o primero, embarazo
enfermedad genital: episodio recurrente, embarazo
enfermedad de la cavidad oral: primer episodio, pacientes inmunocompetentes
enfermedad de la cavidad oral: primer episodio, pacientes inmunocomprometidos
enfermedad de la cavidad oral: episodio recurrente, pacientes inmunocompetentes
enfermedad de la cavidad oral: episodio recurrente, pacientes inmunocomprometidos
enfermedad genital: paciente sexualmente activa o con recurrencias graves frecuentes, inmunocompetente, no embarazada
enfermedad genital: embarazo
enfermedad de la cavidad oral: pacientes con recurrencias graves frecuentes, inmunocompetentes
enfermedad de la cavidad oral: pacientes con recurrencias graves frecuentes, inmunocomprometidos
Contributors
Authors
Benjamin D. Lorenz, MD
Assistant Professor
Division of Hospital Medicine
MedStar Georgetown University Hospital
Washington
DC
Disclosures
BDL declares that he has no competing interests. Since completing the 2024 review, BDL has become an employee of Moderna and has resigned as a contributor.
Acknowledgements
Dr Benjamin D. Lorenz would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Christine Johnson and Dr Anna Wald, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
CJ reports funding from AiCuris; grants from Agenus, Gilead, Genocea, Sanofi, and Vical to conduct clinical research studies; and royalties from Up To Date. AW reports grants from Agenus, Gilead, Genocea, Sanofi, and Vical to conduct clinical research studies. AW receives royalties from Up To Date. AW is an NIH grant recipient (NIH AI30731 and AI071113) and a consultant for Aicuris, Eisai, and Amgen.
Peer reviewers
Giuseppe Pizzo, DDS
Associate Professor
Department of Surgical, Oncological and Oral Sciences
School of Dentistry
University of Palermo
Palermo
Italy
Disclosures
GP declares that he has no competing interests.
Paul Adamson, MD, MPH
Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine
David Geffen School of Medicine
University of California, Los Angeles
Los Angeles
CA
Disclosures
PA declares that he has no competing interests.
Nicholas Van Wagoner, MD, PhD
Associate Professor of Medicine
University of Alabama
Birmingham
AL
Disclosures
NVW declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Morris-Cunnington M, Brown D, Pimenta J, et al. New estimates of herpes simplex virus type 2 seroprevalence in England: 'high' but stable seroprevalence over the last decade. Sex Transm Dis. 2004;31:243-246. Abstract
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Morbidity and mortality weekly report: sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. Jul 2021 [internet publication].Full text
Patel R, Kennedy OJ, Clarke E, et al. 2017 European guidelines for the management of genital herpes. Int J STD AIDS. 2017 Dec;28(14):1366-79.Full text Abstract
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin no. 220: management of genital herpes in pregnancy. May 2020 [internet publication].Full text
British Association for Sexual Health & HIV; Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. Management of genital herpes in pregnancy. Oct 2014 [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Sífilis
- Chancroide
- Linfogranuloma venéreo
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of opportunistic infections in adults and adolescents with HIV
- BASHH summary guidance on testing for sexually transmitted infections, 2023
More GuidelinesPatient information
Herpes genital
Herpes labial
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer