Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- diarrhea
- weight loss
- arthralgia
- supranuclear ophthalmoplegia
Other diagnostic factors
- abdominal pain
- lymphadenopathy
- fever
- steatorrhea
- anemia
- skin darkening
- confusion, memory impairment, altered level of consciousness, or dementia
- apathy
- anxiety, depression, hypomania, psychosis, change in personality
- myoclonic signs
- seizures
- nystagmus
- brisk reflexes, extensor plantar responses, weakness predominating in arm extensors and leg flexors, hypertonia
- amenorrhea, polydipsia, hyperphagia, decreased libido
- ataxia
- headaches
- oculomasticatory and oculofacioskeletal myorhythmias
- hemiparesis
- cranial nerve involvement
- extrapyramidal movement disorder
- peripheral neuropathies
Risk factors
- age >50 years
- male sex
- genetic factors
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- CBC
- serum albumin
- serum CRP
- serum ESR
- upper GI endoscopy
- Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining of duodenal biopsies
- PCR
- Tropheryma whipplei-specific immunohistochemistry
Emerging tests
- electron microscopy
- culture
- serology
Treatment algorithm
patients without CNS involvement
patients with CNS involvement
Contributors
Authors
Thomas Schneider, MD, PhD
Professor
Medical Department I
Charité - University Medicine Berlin
CBF
Berlin
Germany
Disclosures
TS is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Verena Moos, PhD
Scientist
Medical Department I
Charité - University Medicine Berlin
CBF
Berlin
Germany
Disclosures
VM is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Stephen G. Baum, MD
Professor of Medicine
Department of Microbiology and Immunology
Albert Einstein College of Medicine
Bronx
NY
Disclosures
SGB declares that he has no competing interests.
Chris Huston, MD
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Division of Infectious Diseases
University of Vermont
Burlington
VT
Disclosures
CH declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Schneider T, Moos V, Loddenkemper C, et al. Whipple's disease: new aspects of pathogenesis and treatment. Lancet Infect Dis. 2008 Mar;8(3):179-90. Abstract
Fenollar F, Puechal X, Raoult D. Whipple's disease. N Engl J Med. 2007 Jan 4;356(1):55-66.
Dobbins WO. Whipple's disease. Springfield, IL: Thomas; 1987.
Louis ED, Lynch T, Kaufmann P, et al. Diagnostic guidelines in central nervous system Whipple's disease. Ann Neurol. 1996 Oct;40(4):561-8. Abstract
Feurle GE, Junga NS, Marth T. Efficacy of ceftriaxone or meropenem as initial therapies in Whipple's disease. Gastroenterology. 2010 Feb;138(2):478-86; quiz 11-2.Full text Abstract
Feurle GE, Moos V, Bläker H, et al. Intravenous ceftriaxone, followed by 12 or three months of oral treatment with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in Whipple's disease. J Infect. 2013 Mar;66(3):263-70. Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
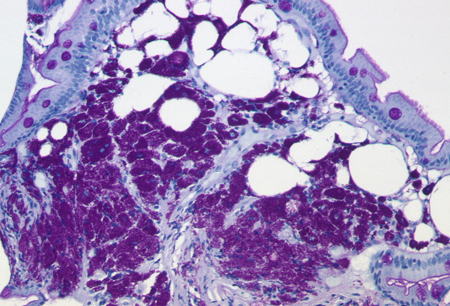
Differentials
- Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis
- Sarcoidosis
- Celiac disease
More DifferentialsPatient information
Diarrhea in adults
Diarrhea in children
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer