Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presencia de factores de riesgo
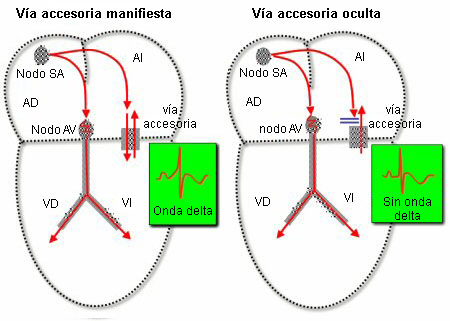
- taquicardia por reentrada auriculoventricular (TRAV)
Other diagnostic factors
- palpitaciones
- mareos
- disnea
- dolor torácico
- fibrilación auricular
- aleteo auricular
- anomalías cardíacas congénitas
- muerte cardíaca súbita
- síncope y presíncope
- taquicardia en el embarazo
Risk factors
- Anomalía de Ebstein
- cardiomiopatía hipertrófica
- prolapso de la válvula mitral
- comunicación interauricular
- comunicación interventricular
- transposición de los grandes vasos
- coartación aórtica
- dextrocardia
- divertículos del seno coronario
- aneurismas de la aurícula izquierda y derecha
- rabdomiomas cardíacos
- síndrome de Marfan
- ataxia de Friedreich
- antecedentes familiares
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- electrocardiograma (ECG) de 12 derivaciones
Tests to consider
- ecocardiograma
- prueba de esfuerzo
- estudio electrofisiológico
Treatment algorithm
inestable: presión arterial <90/60 mmHg, signos de hipoperfusión sistémica o fibrilación auricular inestable
estable: taquicardia de complejo estrecho (ortodrómica de intercambio auriculoventricular)
estable: taquicardia de complejo ancho (antidrómica de intercambio auriculoventricular)
estable: taquicardia con preexcitación por fibrilación auricular o aleteo auricular
estable: taquicardia con preexcitación por taquicardia auricular
tras tratamiento agudo: asintomático
tras tratamiento agudo: sintomático
Contributors
Authors
Hugh Calkins, MD
Professor of Medicine
Director of Electrophysiology
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
Baltimore
MD
Disclosures
HC declares that he is a consultant for Medtronic, Biosense Webster, Abbott, and Boston Scientific.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge our cardiology expert panel member, Dr Fred Kusumoto, for his contribution to this topic.
Professor Hugh Calkins would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr David Frankel, Dr Mithilesh K. Das, and Dr Douglas P. Zipes, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
DF, MKD, and DPZ declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Nicolas Palaskas, MD, FACC
Assistant Professor
University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center
Houston
TX
Disclosures
NP declares that he has no competing interests.
Joseph E. Marine, MD
Associate Professor of Medicine
Director of Electrophysiology
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
Baltimore
MD
Disclosures
JEM declares that he has no competing interests.
Suneet Mittal, MD
Director
Electrophysiology Laboratory
The St. Luke's-Roosevelt Hospital Center
New York
NY
Disclosures
SM declares that he has no competing interests.
Andrew Turley, MB ChB
Cardiology Specialist Registrar
The James Cook University Hospital
Middlesbrough
UK
Disclosures
AT declares that he has no competing interests.
Steve Hsu, MD
Associate Professor
Department of Medicine
Division of Cardiology
University of Florida College of Medicine
Jacksonville
FL
Disclosures
SH declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Brugada J, Katritsis DG, Arbelo E, et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the management of patients with supraventricular tachycardiaThe Task Force for the management of patients with supraventricular tachycardia of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2020 Feb 1;41(5):655-720.Full text Abstract
Zeppenfeld K, Tfelt-Hansen J, de Riva M, et al. 2022 ESC Guidelines for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death. Eur Heart J. 2022 Oct 21;43(40):3997-4126.Full text Abstract
Page RL, Joglar JA, Caldwell MA, et al. 2015 ACC/AHA/HRS guideline for the management of adult patients with supraventricular tachycardia: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67:e27-e115.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Vía auriculofascicular
- Síndrome de Lown-Ganong-Levine
- Vía nodofascicular
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- 2023 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation
- 2022 ESC guidelines for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death
More Guidelinesპაციენტის ბროშურები
Fibrilación auricular: ¿cuáles son las opciones de tratamiento?
Fibrilación auricular: ¿qué es?
მეტი პაციენტის ბროშურებიშედით სისტემაში ან გამოიწერეთ BMJ Best Practice
ამ მასალის გამოყენება ექვემდებარება ჩვენს განცხადებას