Resumo
Definição
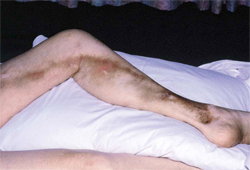
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- presencia de factores de riesgo
- trombosis venosa superficial (TVS), trombosis venosa profunda o embolia pulmonar previas
- enrojecimiento/eritema de la piel suprayacente
- piel suprayacente caliente
- dolor/sensible a la palpación sobre la vena afectada
- inflamación/edema del área circundante
- masa palpable similar a un cordón
- desarrollo de los síntomas en horas y días
- signos/síntomas de trombosis venosa profunda (TVP) o embolia pulmonar (EP) concomitantes
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- venas varicosas
- antecedentes de trastornos trombofílicos
- enfermedades autoinmunes (p. ej., enfermedad de Behcet y enfermedad de Buerger)
- instrumentación venosa reciente (p. ej., escleroterapia)
- administración de fármacos por vía intravenosa y canulación venosa reciente
- febrícula
- cambios en la pigmentación
Fatores de risco
- venas varicosas
- trastornos trombofílicos
- enfermedades autoinmunes (p. ej., enfermedad de Behcet y enfermedad de Buerger)
- antecedentes de trombosis venosa superficial (TVS)
- sexo femenino
- escleroterapia
- cateterismo intravenoso
- neoplasia maligna
- embarazo
- uso de anticonceptivos orales (ACO) y tratamiento de reposición hormonal
- edad avanzada
- antecedentes previos de tromboembolia venosa (TEV), incluidas trombosis venosa profunda y EP
- obesidad
- inmovilización prolongada (p. ej., viajes en avión de larga distancia)
- Tipo de sangre
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- ecografía Doppler
Investigações a serem consideradas
- biopsia
- angiografía por tomografía computarizada (TC) pulmonar
- gammagrafía de ventilación y perfusión (VQ)
- angiografía pulmonar convencional
- evaluación para detectar neoplasia maligna
- cribado de trombofilia
Algoritmo de tratamento
extensión a la vena femoral o a la vena poplítea, trombo ≤3 de la unión safenofemoral o safenopoplítea, o TVP o EP concomitantes
no embarazadas: TVS de ≥5 cm de longitud dentro de la vena superficial axial y a >3 cm de la unión safenofemoral o safenopoplítea
no embarazadas: TVS de <5 cm de longitud dentro de la vena superficial axial o trombo solo dentro de las venas varicosas tributarias
embarazadas: TVS (de cualquier tamaño) dentro de la vena axial o tributaria
vena safena incompetente con venas varicosas asociadas o TVS recurrente
Colaboradores
Autores
Sherry Scovell, MD, FACS
Vascular and Endovascular Surgeon
Massachusetts General Hospital
Assistant Professor of Surgery, Part Time
Harvard Medical School
Boston
MA
Declarações
SS is an author for UpToDate, which is compensated. SS declares that she has no conflicts of interest with medical or pharmaceutical companies.
Agradecimentos
Dr Sherry Scovell would like to gratefully acknowledge Professor Vicky Tagalakis, a previous contributor to this topic.
Declarações
VT has received reimbursement for advisory board work for Servier and Pzifer. Both of these companies are makers of anticoagulants. VT has received an investigator-initiated grant from Sanofi, manufacturer of Enoxaparin.
Revisores
Francois Becker, MD, PhD
Consultant
Division of Angiology and Hemostasis
University Hospital of Geneva
Geneva
Switzerland
Declarações
FB declares that he has no competing interests.
Michael Bromberg, MD, PhD
Professor of Medicine
Section of Hematology
Director of Hematologic Malignancies
Temple University School of Medicine
Philadelphia
PA
Declarações
MB declares that he has no competing interests.
Louis Aledort, MD
The Mary Weinfeld Professor of Clinical Research in Hemophilia
Mount Sinai School of Medicine
New York
NY
Declarações
LA declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Stevens SM, Woller SC, Kreuziger LB, et al. Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: second update of the CHEST guideline and expert panel report. Chest. 2021 Dec;160(6):e545-608.Texto completo Resumo
Kakkos SK, Gohel M, Baekgaard N, et al. Editor's Choice - European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2021 clinical practice guidelines on the management of venous thrombosis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021 Jan;61(1):9-82.Texto completo Resumo
Thrombosis Canada. Superficial thrombophlebitis, superficial vein thrombosis. Aug 2023 [internet publication].Texto completo
Di Nisio M, Wichers IM, Middeldorp S. Treatment for superficial thrombophlebitis of the leg. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 25;(2):CD004982.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Trombosis venosa profunda
- Celulitis
- Linfedema
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2023 clinical practice guidelines on antithrombotic therapy for vascular diseases
- Superficial thrombophlebitis, superficial vein thrombosis
Mais DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Trombosis venosa profunda
Varices: ¿qué son?
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal