Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presencia de factores de riesgo
- tos
- disnea
Other diagnostic factors
- fiebre
- dolor torácico pleurítico
- taquipnea
- aliento fétido
- crepitaciones
- esputo purulento o espumoso
- antecedentes de vómitos
Risk factors
- quimiorradiación en cánceres de cabeza y cuello
- alteración del estado mental
- disfunción en la deglución
- enfermedad gastrointestinal
- intubación o sonda de traqueostomía
- edad avanzada
- higiene bucal deficiente
- sonda de alimentación
- posición en decúbito
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- saturación de O2
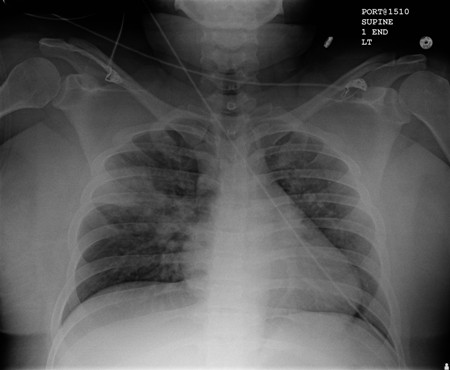
- radiografía del tórax (RT)
- hemograma completo (HC)
- tinción de Gram del esputo
- cultivo de esputo
Investigations to consider
- ecografía pulmonar a pie de cama
- GSA
- broncoscopia
Treatment algorithm
todos los pacientes
Contributors
Authors
Michael J. Lanspa, MD, MS
Adjunct Associate Professor
Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine
Intermountain Medical Center
University of Utah
Salt Lake City
UT
Disclosures
MJL declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Michael J. Lanspa would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Richard Kanner and Dr Krishna Sundar, previous contributors to this topic. DK and KS declares that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Toby Maher, MB, PhD, MRCP
Consultant Respiratory Physician
Department of Respiratory Medicine
Royal Brompton Hospital
London
UK
Disclosures
TM has received research funding from the Wellcome Trust and GlaxoSmithKline. He has acted as a paid consultant to GSK, Actelion, and Respironies.
Feras Hawari, MD
Chief of Pulmonary and Critical Care
King Hussein Cancer Center
Amman
Jordan
Disclosures
FH declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Metlay JP, Waterer GW, Long AC, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia. An official clinical practice guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Oct 1;200(7):e45-e67.Full text Abstract
American Society of Anesthesiologists. Practice guidelines for preoperative fasting and the use of pharmacologic agents to reduce the risk of pulmonary aspiration: application to healthy patients undergoing elective procedures: an updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Preoperative Fasting and the Use of Pharmacologic Agents to Reduce the Risk of Pulmonary Aspiration. Anesthesiology. 2017 Mar;126(3):376-93.Full text Abstract
Kalil AC, Metersky ML, Klompas M, et al. Management of adults with hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia: 2016 clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the American Thoracic Society. Clin Infect Dis. 2016 Sep 1;63(5):e61-e111.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Neumonitis por aspiración
- Atelectasia
- Edema pulmonar
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Pneumonia in adults: diagnosis and management
- Stroke and transient ischaemic attack in over 16s: diagnosis and initial management
More GuidelinesPatient information
Neumonía
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer