Resumen
Definición
Anamnesis y examen
Principales factores de diagnóstico
- presencia de factores de riesgo
- erupción polimorfa
- inyección conjuntival
- mucositis
- cambios cutáneos en las extremidades periféricas
- linfadenopatía cervical
- aneurismas en la arteria coronaria
- fiebre e irritabilidad extrema
Otros factores de diagnóstico
- pericarditis con derrame
- insuficiencia cardíaca congestiva
- edema o dolor en las articulaciones
- ronquera
- manifestaciones neurológicas
- manifestaciones gastrointestinales
- manifestaciones urológicas
- otras manifestaciones dermatológicas
Factores de riesgo
- linaje asiático
- edad: de 3 meses a 4 años
- sexo masculino
Pruebas diagnósticas
Primeras pruebas diagnósticas para solicitar
- hemograma completo (HC)
- velocidad de sedimentación globular (VSG)
- proteína C-reactiva sérica
- ecocardiograma
- pruebas de función hepática (PFH) séricas
- análisis de orina
- electrocardiograma
Pruebas diagnósticas que deben considerarse
- radiografía del tórax (RT)
- ultrasonografía de la vesícula biliar
- ultrasonografía de testicular
- punción lumbar
- angiografía por tomografía computada
- angiografía por resonancia magnética (ARM)
- angiografía y cateterismo cardíaco
Pruebas emergentes
- pruebas de péptidos natriuréticos
Algoritmo de tratamiento
presentación ≤10 días desde el inicio; o presentación >10 días desde el inicio con evidencia de inflamación en curso
presentación >10 días desde el inicio sin evidencia de inflamación en curso
después del episodio inicial: el puntaje Z siempre <2; sin afectación en ningún momento
desde el episodio inicial: puntaje Z ≥2.0 a <2.5; solo dilación
desde el episodio inicial: puntuación Z ≥2.5 a <5.0; aneurisma de pequeño tamaño
desde el episodio inicial: el puntaje Z ≥5 a <10 (con dimensión luminal absoluta <8 mm); aneurisma de tamaño medio
después del episodio inicial: puntaje Z ≥10 o diámetro luminal absoluto ≥8 mm; aneurisma de gran tamaño o gigante
Colaboradores
Autores
Paul Brogan, BSc(Hon), MBChB(Hon), FRCPCH, MSc, PhD
Professor of vasculitis
University College London
London
UK
Divulgaciones
PB is chief investigator of the KDCAAP trial, results pending; trustee of Societi, a patient KD organisation; and is an author of several references cited in this topic.
Kirsty McLellan, BMedSci, MBChB, MRCPCH
Specialist Registrar in Paediatric Rheumatology
Great Ormond Street Hospital
London
UK
Divulgaciones
KM declares she has no competing interests.
Agradecimientos
Dr Paul Brogan and Dr Kirsty McLellan would like to gratefully acknowledge Professor Abraham Gedalia and Dr James Krulisky, previous contributors to this topic.
Divulgaciones
AG declares that he has no competing interests. JK declares that he is a paid consultant for Axia Medical Solutions, a small skincare company from Carlsbad, CA.
Revisores por pares
Michael Levin, null
Professor of International Child Health
Imperial College London
London
Divulgaciones
ML declares that he has no competing interests.
Kirsten Bourke Dummer, MD
Clinical Professor, Pediatrics
Division of Pediatric Cardiology
UC San Diego/Rady Children’s Hospital
San Diego
CA
Divulgaciones
KBD declares that she has no competing interests.
David Burgner, BSc(Hons), MBChB, MRCP, MRCPCH, FRACP, DTMH, PhD
Principal Research Fellow
Murdoch Childrens Research Institute
The Royal Children’s Hospital
Victoria
Australia
Divulgaciones
DB has received competitive research funding from the National Heart Foundation Australia and from the Agency for Science, Technology and Research of the Singapore Government. He is co-inventor on a patent related to diagnostics submitted through the Genome Institute of Singapore.
Agradecimiento de los revisores por pares
Los temas de BMJ Best Practice se actualizan de forma continua de acuerdo con los desarrollos en la evidencia y en las guías. Los revisores por pares listados aquí han revisado el contenido al menos una vez durante la historia del tema.
Divulgaciones
Las afiliaciones y divulgaciones de los revisores por pares se refieren al momento de la revisión.
Referencias
Artículos principales
McCrindle BW, Rowley AH, Newburger JW, et al; American Heart Association. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a scientific statement for health professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017 Apr 25;135(17):e927-99.Texto completo Resumen
de Graeff N, Groot N, Ozen S, et al. European consensus-based recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of Kawasaki disease - the SHARE initiative. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019 Apr 1;58(4):672-82.Texto completo Resumen
Jone PN, Tremoulet A, Choueiter N, et al. Update on diagnosis and management of Kawasaki disease: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2024 Dec 3;150(23):e481-500.Texto completo Resumen
Gorelik M, Chung SA, Ardalan K, et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology/Vasculitis Foundation guideline for the management of Kawasaki disease. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2022 Apr;74(4):538-48. Resumen
Artículos de referencia
Una lista completa de las fuentes a las que se hace referencia en este tema está disponible para los usuarios con acceso a todo BMJ Best Practice.
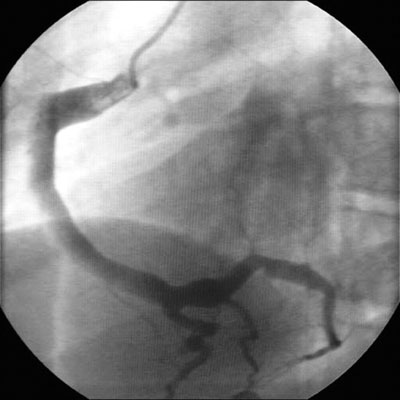
Diferenciales
- infecciones estafilocócicas o estreptocócicas
- Artritis idiopática juvenil sistémica (AIJ sistémica)
- Escarlatina
Más DiferencialesGuías de práctica clínica
- Update on diagnosis and management of Kawasaki disease: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association
- European consensus-based recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of Kawasaki disease - the SHARE initiative
Más Guías de práctica clínicaInicie sesión o suscríbase para acceder a todo el BMJ Best Practice
El uso de este contenido está sujeto a nuestra cláusula de exención de responsabilidad