Resumen
Definición
Anamnesis y examen
Principales factores de diagnóstico
- presencia de factores de riesgo
- antecedentes de exposición reciente a la heparina
- antecedentes de TIH
- ausencia de enfermedades y medicamentos que causan trombocitopenia
- antecedentes de cirugía o traumatismo recientes
- características consecuentes con un evento tromboembólico venoso o arterial (p. ej., embolia pulmonar [EP], trombosis venosa profunda [TVP], accidente cerebrovascular, infarto de miocardio [IM]).
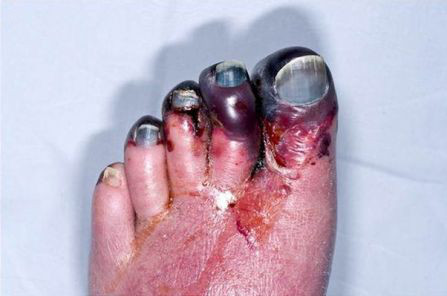
- necrosis en los lugares de las inyecciones de heparina
Otros factores de diagnóstico
- ausencia de sangrado
- signos de necrosis hemorrágica suprarrenal
- reacción sistémica aguda
- signos de gangrena venosa en las extremidades
Factores de riesgo
- exposición reciente a la heparina (dentro de los últimos 100 días)
- cirugía cardiovascular u ortopédica reciente
- sexo femenino
Pruebas diagnósticas
Primeras pruebas diagnósticas para solicitar
- hemograma completo (HC)
Pruebas diagnósticas que deben considerarse
- Índice 4T
- ensayo con antígenos de trombocitopenia inducida por heparina (TIH)
- Ensayo funcional de TIH
- estudios de coagulación
- ultrasonido Doppler venoso
- angiografía pulmonar por tomografía computarizada (APTC)
- gammagrafía de ventilación-perfusión, (gammagrafía de V/P)
- flebografía por tomografía computarizada cerebral
- venografía por resonancia magnética (cabeza)
Algoritmo de tratamiento
sospecha de TIH con índice 4T ≥4, o TIH aguda confirmada
sospecha de trombocitopenia inducida por heparina (TIH) con índice 4T ≤3
recuperación plaquetaria (TIH A subaguda)
TIH remota
Colaboradores
Autores
Lori-Ann Linkins, MD, MSc(Clin Epi), FRCPC
Associate Professor
Department of Medicine
McMaster University
Thrombosis Consultant
Juravinski Hospital and Cancer Centre
Hamilton
Ontario
Canada
Divulgaciones
LL is an author of several references cited in this topic.
Revisores por pares
Jeffrey S. Wasser, MD
Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine
Acting Associate Chair of the Division of Hematology and Medical Oncology
University of Connecticut School of Medicine
Farmington
CT
Divulgaciones
JSW declares that he has no competing interests.
Henry Watson, MD, FRCP, FRCPath
Consultant Haematologist
Aberdeen Royal Infirmary
Foresterhill Health Campus
Aberdeen
UK
Divulgaciones
HW declares that he has no competing interests.
Simon Davidson, MPhil
Clinical Scientist
Royal Brompton Hospital
Honorary Clinical Lecturer
Imperial College London
London
UK
Divulgaciones
SD is a consultant for Mitsubishi Pharma, the manufacturer of argatroban.
Agradecimiento de los revisores por pares
Los temas de BMJ Best Practice se actualizan de forma continua de acuerdo con los desarrollos en la evidencia y en las guías. Los revisores por pares listados aquí han revisado el contenido al menos una vez durante la historia del tema.
Divulgaciones
Las afiliaciones y divulgaciones de los revisores por pares se refieren al momento de la revisión.
Referencias
Artículos principales
Warkentin T, Kelton J. Temporal aspects of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1286-1292.Texto completo Resumen
Cuker A, Arepally GM, Chong BH, et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood Adv. 2018 Nov 27;2(22):3360-92.Texto completo Resumen
Linkins LA, Dans AL, Moores LK, et al. Treatment and prevention of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis (9th ed). American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2012 Feb;141(2 Suppl):e495S-e530S.Texto completo Resumen
Watson H, Davidson S, Keeling D, et al. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: second edition. Br J Haematol. 2012 Dec;159(5):528-40.Texto completo Resumen
Artículos de referencia
Una lista completa de las fuentes a las que se hace referencia en este tema está disponible para los usuarios con acceso a todo BMJ Best Practice.
Diferenciales
- Estado postoperatorio
- Púrpura trombótica trombocitopénica
- Púrpura trombocitopénica inducida por fármacos
Más DiferencialesGuías de práctica clínica
- Guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
- Treatment and prevention of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (9th ed)
Más Guías de práctica clínicaInicie sesión o suscríbase para acceder a todo el BMJ Best Practice
El uso de este contenido está sujeto a nuestra cláusula de exención de responsabilidad