Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- rapid onset of signs and symptoms (acute septic cavernous sinus thrombosis)
- headache
- fever
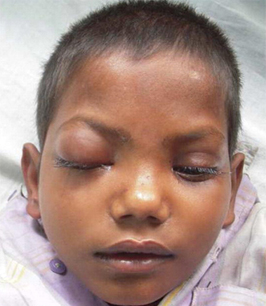
- periorbital edema
- chemosis and proptosis
- lateral gaze palsy
- ophthalmoplegia
- profound sepsis (acute septic cavernous sinus thrombosis [CST])
Other diagnostic factors
- ptosis and mydriasis
- papilledema and/or retinal-vein dilatation
- decreased corneal reflex
- hypo- or hyperesthesia in the distribution of the ophthalmic and maxillary nerves
- mental state changes (e.g., confusion, drowsiness, coma)
- clinically detectable primary infection site
- meningismus (nuchal rigidity, photophobia, and headache)
- positive Kernig or Brudzinski signs
- seizures
- loss of visual acuity
Risk factors
- recent history of acute sinusitis
- history of facial infections
- history of periorbital infection
- history of otitis media, mastoiditis, or petrositis
- history of dental or oral infection
- history of sepsis
- immunosuppression
- genetic prothrombotic condition
- acquired and other prothrombotic states
- history of head and neck trauma
- use of oral contraceptives
- pregnant or postpartum
- history of malignancy
- history of recent head or neck surgery
- vascular abnormalities
- ulcerative colitis
- volume depletion
- heroin overdose
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- CBC
- contrast-enhanced high-resolution CT of head
- contrast-enhanced MRI of head
- blood culture
- microscopy and culture of suppurative fluid or tissue from primary infective source
- antiphospholid and anticardiolipin antibodies
- protein S and protein C
- antithrombin III
- factor V Leiden
- hemoglobin electrophoresis
- D-dimer level
Tests to consider
- lumbar puncture with cerebrospinal fluid analysis
Treatment algorithm
suspected cavernous sinus thrombosis (CST)
confirmed septic cavernous sinus thrombosis (CST): without hemorrhagic complications
confirmed septic cavernous sinus thrombosis (CST): with hemorrhagic complications
confirmed aseptic cavernous sinus thrombosis (CST): without hemorrhagic complications
confirmed aseptic cavernous sinus thrombosis (CST): with hemorrhagic complications
Contributors
Authors
Jayant Pinto, MD
Associate Professor of Surgery
Section of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery
University of Chicago
IL
Disclosures
JMP has received funds from Regeneron, Sanofi, and Optinose for speaker's bureau and advisory boards. He served as a site investigator for Regeneron, Sanofi, and Upstream Bio.
Mohamad R. Chaaban, MD, MSCR, MBA
Associate Professor
Cleveland Clinic
Lerner College of Medicine at Case Western Reserve University
Cleveland
OH
Disclosures
MRC has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
David Rowed, MD
Division of Neurosurgery
University of Toronto
Toronto
Ontario
Canada
Disclosures
DR declares that he has no competing interests.
Louis R. Caplan, MD
Lecturer in Neurology
Hospital Chief
Cerebrovascular/Stroke Division
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Division of Cerebrovascular/Stroke
Boston
MA
Disclosures
LRC declares that he has no competing interests.
Sorabh Khandelwal, MD
Clinical Associate Professor of Emergency Medicine
Ohio State University
Columbus
OH
Disclosures
SK declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Ebright JR, Pace MT, Niazi AF. Septic thrombosis of the cavernous sinuses. Arch Intern Med. 2001 Dec 10-24;161(22):2671-6.Full text Abstract
Caranfa JT, Yoon MK. Septic cavernous sinus thrombosis: a review. Surv Ophthalmol. 2021 Nov-Dec;66(6):1021-30. Abstract
Bhatia K, Jones NS. Septic cavernous sinus thrombosis secondary to sinusitis: are anticoagulants indicated? A review of the literature. J Laryngol Otol. 2002 Sep;116(9):667-76. Abstract
American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: headache. 2022 [internet publication].Full text
American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: orbits, vision, and visual loss. 2017 [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Periorbital or orbital cellulitis
- Superior orbital fissure syndrome
- Orbital apex syndrome
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- ACR appropriateness criteria: cerebrovascular diseases-stroke and stroke-related conditions
- ACR appropriateness criteria: headache
More GuidelinesPatient information
Meningitis and septicemia
Preventing another stroke
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer