Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) recipient
- human leukocyte antigen (HLA) mismatch and unrelated donor
- parous female donor
- female donor with male recipient
- new-onset painful mouth sores
- hyperpigmented skin lesions
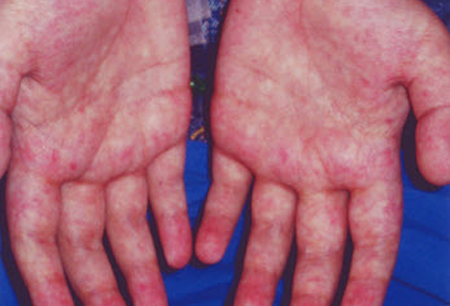
- diffuse maculopapular rash
- genital signs and symptoms
- nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, profuse diarrhea, and anorexia
Other diagnostic factors
- joint stiffness or tightness
- day +21 to day +25 after HCT
- cyclophosphamide + total body irradiation (Cy/TBI) conditioning regimen
- peripheral blood stem cell transplant
- dry, gritty, and painful eyes
- jaundice
- hepatomegaly
- scleroderma
Risk factors
- HLA mismatch and unrelated donor
- prior acute GVHD
- recipient or donor in older age group
- female donor with male recipient
- parous female donor
- type and stage of underlying malignant condition
- high-intensity conditioning radiation regimen
- peripheral blood stem cell transplant
- donor lymphocyte infusion (DLI)
- absent or suboptimal GVHD prophylaxis
- white or black race
- cytomegalovirus (CMV) seropositive
- splenectomy
- low performance status score
- low socioeconomic status
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- CBC
- serum electrolytes
- liver functions tests
- urinalysis
- urine culture
- blood culture
- stool culture
- viral polymerase chain reaction (PCR) studies
Tests to consider
- CT abdomen
- Doppler ultrasound of the liver
- tissue biopsy (skin, gastrointestinal [GI] tract, liver, or lung)
- pulmonary function tests
- high-resolution CT chest
- bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) and culture
- echocardiogram
- barium swallow or upper gastrointestinal endoscopy
- 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) scan
Emerging tests
- serum biomarkers
Treatment algorithm
hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) recipient
acute: grade I
acute: grade II-IV
chronic
Contributors
Authors
Sung Won Choi, MD, MS

Professor
Department of Pediatrics
Division of Pediatric Hematology Oncology/Blood and Marrow Transplantation
University of Michigan
Ann Arbor
MI
Disclosures
SWC is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Lyndsey Runaas, MD

Assistant Professor, Hematology and Oncology
Division of Hematology/Oncology
Medical College of Wisconsin
Milwaukee
WI
Disclosures
LR declares that she has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Sung Choi and Dr Lyndsey Runaas would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Pavan Reddy, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
PR is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Corey Cutler, MD, MPH, FRCPC
Associate Professor of Medicine
Harvard Medical School
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute
Boston
MA
Disclosures
CC declares that he has no competing interests.
Waseem Qasim, BMedSci (Hons), MBBS, MRCP (UK), MRCPCH, PhD
Senior Lecturer
Institute of Child Health
Consultant in Paediatric Immunology & Bone Marrow Transplantation
Great Ormond Street Hospital
London
UK
Disclosures
WQ declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Jagasia MH, Greinix HT, Arora M, et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. The 2014 Diagnosis and Staging Working Group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015 Mar;21(3):389-401.e1.Full text Abstract
Penack O, Marchetti M, Aljurf M, et al. Prophylaxis and management of graft-versus-host disease after stem-cell transplantation for haematological malignancies: updated consensus recommendations of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Lancet Haematol. 2024 Feb;11(2):e147-59. Abstract
Dignan FL, Amrolia P, Clark A, et al. Diagnosis and management of chronic graft-versus-host disease. Br J Haematol. 2012 Jul;158(1):46-61.Full text Abstract
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: hematopoietic cell transplantation [internet publication].Full text
Dignan FL, Clark A, Amrolia P, et al. Diagnosis and management of acute graft-versus-host disease. Br J Haematol. 2012 Jul;158(1):30-45.Full text Abstract
Carpenter PA, Kitko CL, Elad S, et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: V. The 2014 Ancillary Therapy and Supportive Care Working Group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015 Jul;21(7):1167-87.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Drug rash
- Radiation or chemotherapy-induced rash
- Bacterial gastroenteritis
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: hematopoietic cell transplantation
- Prophylaxis and management of graft-versus-host disease after stem-cell transplantation for haematological malignancies: updated consensus recommendations
More GuidelinesCalculators
The Minnesota Refined Acute GvHD Risk Score
More CalculatorsLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer