Resumen
Definición
Anamnesis y examen
Principales factores de diagnóstico
- identification of the snake
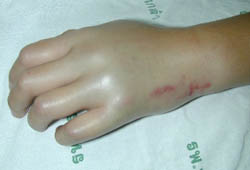
- local redness, swelling, tenderness, and pain at wound site
- blurred or double vision
- shortness of breath
- difficulty swallowing
- hypotension
- tachypnea
- tachycardia
- puncture marks, fang marks
- bulbar weakness/paralysis
- stridor
- hemorrhage
- quadriplegia/locked-in syndrome
Otros factores de diagnóstico
- nausea and vomiting
- malaise, generalized weakness or dizziness
- perioral tingling or numbness
- urticaria
- tremors
Factores de riesgo
- male sex
- alcohol consumption
- intentional snake encounter
Pruebas diagnósticas
Primeras pruebas diagnósticas para solicitar
- prothrombin time, PTT, fibrinogen, and D-dimer
- CBC
- electrolytes, BUN, and creatinine
- arterial blood gas
- creatine kinase (CK)
- lactate
- urinalysis
- ECG
- chest x-ray
- wound x-ray
- negative inspiratory force (NIF) test
Pruebas diagnósticas que deben considerarse
- CT/MRI
- compartment pressure
- central venous line with central venous pressure (CVP) transduction
- arterial line with pressure transduction
Algoritmo de tratamiento
presumed snakebite
confirmed snakebite
Colaboradores
Autores
David Vearrier, MD, MPH, FAAEM, FACMT, FAACT

Professor of Emergency Medicine
Division of Medical Toxicology
Department of Emergency Medicine
Program Director, Medical Toxicology Fellowship
Associate Program Director, Preventive Medicine Residency
Co-Director, Student and Employee Health
Department of Preventive Medicine
University of Mississippi Medical Center
Jackson
MS
Declarações
DV declares that he has no competing interests.
Agradecimentos
Prof. David Vearrier would like to gratefully acknowledge Prof. Michael Greenberg, previous contributor to this topic. MG declared that he had no competing interests.
Revisores
Scott Phillips, MD
Associate Clinical Professor of Medicine
Department of Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology
University of Colorado
Health Science Center
Denver
CO
Disclosures
SP has a professional relationship with Michael Greenberg, one of the original contributors to this topic. They are partners in a private consulting company. SP does not receive money from him, nor does he receive money from SP.
Donna Seger, MD
Medical Director TN Poison Center
Associate Professor of Medicine and Emergency Medicine
Vanderbilt University Medical Center
Nashville
TN
Disclosures
DS declares that she has no competing interests.
Senanayake Kularatne, MBBS, MD, MRCP, FRCP, FCCP
Professor
Department of Medicine
Peredeniya University
Sri Lanka
Disclosures
SK declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Kanaan NC, Ray J, Stewart M, et al. Wilderness Medical Society practice guidelines for the treatment of pitviper envenomations in the United States and Canada. Wilderness Environ Med. 2015 Dec;26(4):472-87.Full text Abstract
Hewett Brumberg EK, Douma MJ, Alibertis K, et al. 2024 American Heart Association and American Red Cross guidelines for first aid. Circulation. 2024 Dec 10;150(24):e519-79.Full text Abstract
Lavonas EJ, Ruha AM, Banner W, et al. Unified treatment algorithm for the management of crotaline snakebite in the United States: results of an evidence-informed consensus workshop. BMC Emerg Med. 2011 Feb 3;11:2.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Anaphylaxis
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- 2024 American Heart Association and American Red Cross guidelines for first aid
- Wilderness Medical Society practice guidelines for the treatment of pitviper envenomations in the US and Canada
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer