Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
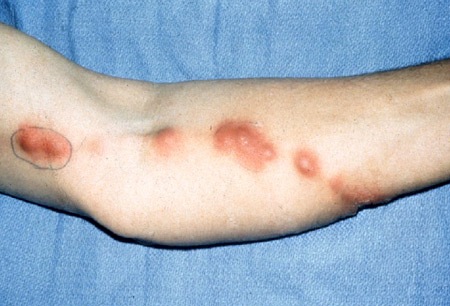
- primary skin lesion
- nodular lymphangitis lesions
Other diagnostic factors
- respiratory symptoms
- joint swelling/erythema
- male 30 to 60 years old
- fever
- lymphadenopathy
- meningitis-like symptoms
Risk factors
- trauma to the skin
- outdoor occupation/hobbies
- animal bites and scratches
- alcohol use disorder
- diabetes mellitus
- HIV/AIDS
- COPD
- corticosteroid treatment
- chemotherapy in patients with hematologic malignancy
- hematopoietic stem cell/solid organ transplantation
- tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha inhibitor therapy
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- skin lesion fungal culture
- skin lesion histopathology (Gomori methenamine silver, periodic acid-Schiff staining)
- CBC
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- joint x-ray
- fungal culture of arthrocentesis synovial fluid
- sputum or bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fungal culture
- lumbar puncture for cerebrospinal fluid analysis
- cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) fungal culture
- fungal blood culture
Tests to consider
- synovial tissue biopsy for fungal culture
- synovial tissue histopathology (Gomori methenamine silver, periodic acid-Schiff staining)
- bronchial biopsy fungal culture
- bronchial biopsy histopathology
- CXR
- CT of chest
- serum itraconazole levels
- serum BUN
- serum creatinine
- LFTs
Emerging tests
- immunohistochemical staining
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Treatment algorithm
nonpregnant: lymphocutaneous/cutaneous
nonpregnant: extracutaneous mild/moderate disease
nonpregnant: extracutaneous severe/life-threatening disease
pregnant: cutaneous
pregnant: lymphocutaneous
pregnant: extracutaneous
Contributors
Authors
Michail Lionakis, MD, ScD
Chief
Fungal Pathogenesis Section
Laboratory of Clinical Immunology and Microbiology
National Institutes of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
National Institutes of Health
Bethesda
MD
Disclosures
ML declares that he has no competing interests.
John E. Bennett, MD
Chief
Clinical Mycology Section
Laboratory of Clinical Immunology and Microbiology
National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
National Institutes of Health
Bethesda
MD
Disclosures
JEB declares that he has no competing interests.
Revisores por pares
George Samonis, MD
Professor of Internal Medicine/Infectious Diseases
University of Crete
Department of Internal Medicine
Gallos University Campus
Crete
Greece
Divulgaciones
GS declares that he has no competing interests.
Amy Xu, MD, MA
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Section of Dermatology
University of Chicago
Chicago
IL
Divulgaciones
AX declares that she has no competing interests.
Agradecimiento de los revisores por pares
Los temas de BMJ Best Practice se actualizan de forma continua de acuerdo con los desarrollos en la evidencia y en las guías. Los revisores por pares listados aquí han revisado el contenido al menos una vez durante la historia del tema.
Divulgaciones
Las afiliaciones y divulgaciones de los revisores por pares se refieren al momento de la revisión.
Referencias
Artículos principales
Rex JH, Okhuysen PC. Sporothrix schenckii. In Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Principles and practice of infectious diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier, 2020: 3131-6.
Orofino-Costa R, Macedo PM, Rodrigues AM, et al. Sporotrichosis: an update on epidemiology, etiopathogenesis, laboratory and clinical therapeutics. An Bras Dermatol. 2017 Sep-Oct;92(5):606-20.Texto completo Resumen
Kauffman CA, Bustamante B, Chapman SW, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of sporotrichosis: 2007 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2007 Nov 15;45(10):1255-65.Texto completo Resumen
Sharkey-Mathis PK, Kauffman CA, Graybill JR, et al. Treatment of sporotrichosis with itraconazole. NIAID Mycoses Study Group. Am J Med. 1993 Sep;95(3):279-85. Resumen
Artículos de referencia
Una lista completa de las fuentes a las que se hace referencia en este tema está disponible para los usuarios con acceso a todo BMJ Best Practice.
Diferenciales
- Primary cutaneous nocardiosis
- Cutaneous Mycobacterium marinum infection
- Cutaneous leishmaniasis
Más DiferencialesInicie sesión o suscríbase para acceder a todo el BMJ Best Practice
El uso de este contenido está sujeto a nuestra cláusula de exención de responsabilidad