Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
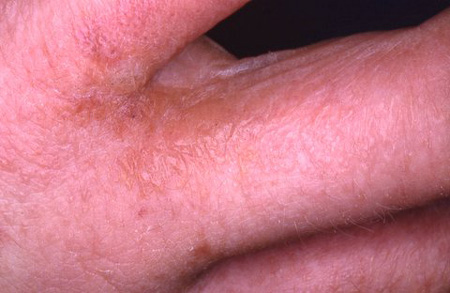
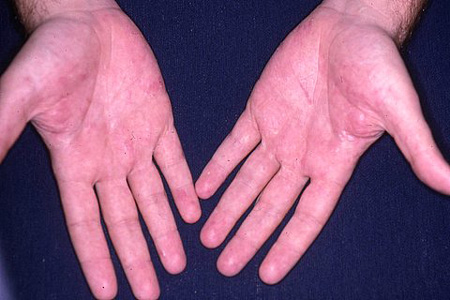
- skin lesions
- pruritus
Other diagnostic factors
- hyperhidrosis
- recurrent eruptions
- pain
Risk factors
- exposure to irritants
- atopy
- metal allergy
- hyperhidrosis
- emotional stress
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- clinical diagnosis
Tests to consider
- skin biopsy
- potassium hydroxide (KOH)
- patch testing
- skin scraping
Treatment algorithm
all patients
Contributors
Authors
Peggy A Wu, MD, MPH, FAAD
Professor of Clinical Dermatology
University of California Davis
Sacramento
CA
Disclosures
PAW declares that she has received royalties for contributing to UpToDate. She is also a contributor for a National Comprehensive Cancer Network guideline although she receives no compensation for this.
Victor Huang, MD, FAAD
Associate Professor of Clinical Dermatology
Dermatology
University of California Davis
Sacramento
CA
Disclosures
VH declares that she has received royalties for contributing to UpToDate and has served on an advisory board for the Opzelura in the treatment of vitiligo.
Acknowledgements
Dr Peggy Wu and Dr Victor Huang would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Andrea Bershow, Dr Erin M. Warshaw and Dr Sabra M. Lofgren, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
AB, EMW and SML declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Kachiu Cecilia Lee, MD, MPH
Assistant Professor
Department of Dermatology
Brown Medical School
Providence
Rhode Island
Disclosures
KCL declares that she has no competing interests.
Gerard Guillet, MD
Professor of Dermatology
Department of Dermatology and Allergology
University Hospital Poitiers
Poitiers
France
Disclosures
GG declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Agner T, Elsner P. Hand eczema: epidemiology, prognosis and prevention. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 Jan;34 Suppl 1:4-12.Full text Abstract
Elsner P, Agner T. Hand eczema: treatment. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 Jan;34 Suppl 1:13-21.Full text Abstract
Jacob PT, Marie LAS, Jose HA, et al. Guidelines for diagnosis, prevention and treatment of hand eczema. Contact Dermatitis. 2022 May;86(5):357-78. Abstract
Christoffers WA, Coenraads PJ, Svensson Å, et al. Interventions for hand eczema. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Apr 26;4(4):CD004055.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
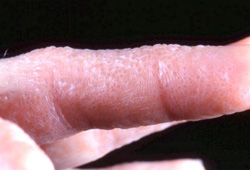
Differentials
- Tinea manuum/pedis
- Palmoplantar psoriasis
- Allergic contact dermatitis
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Guidelines for diagnosis, prevention and treatment of hand eczema
More GuidelinesPatient information
Dermatitis
Eczema
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer