Proteinuria is common, and prevalence increases with kidney disease progression. It is often diagnosed incidentally on routine dipstick testing of urine samples; an appropriate index of suspicion is required to specifically request urinalysis for protein measurement.
Average daily urinary protein excretion in adults is 80 mg/day, with normal excretion considered to be <150 mg/day.
Albumin represents approximately 15% of the daily urinary protein excretion in healthy people, with other plasma proteins (e.g., immunoglobulins, beta-2-microglobulin) and Tamm-Horsfall protein constituting the remaining 85%.
Proteinuria varies in amount and may be transient or persistent.[1]Viswanathan G, Upadhyay A. Assessment of proteinuria. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2011 Jul;18(4):243-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21782130?tool=bestpractice.com
[2]Montañés Bermúdez R, Gràcia García S, Pérez Surribas D, et al. Consensus document. Recommendations on assessing proteinuria during the diagnosis and follow-up of chronic kidney disease. Nefrologia. 2011;31(3):331-45.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21780317?tool=bestpractice.com
It is important to distinguish benign, self-limiting etiologies from more significant illness. New-onset proteinuria with features of systemic disease (e.g., progressive renal dysfunction, other organ system abnormalities) should be evaluated as soon as possible.
Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) defines chronic kidney disease (CKD) as abnormalities of kidney structure or function, present for ≥3 months.[3]Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes. KDIGO 2024 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Apr 2024 [internet publication].
https://kdigo.org/guidelines/ckd-evaluation-and-management
Albuminuria (albumin-to-creatinine ratio ≥30 mg/g) is one of the markers of kidney damage. CKD is classified based on cause, glomerular filtration rate (GFR) category and albuminuria category.[3]Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes. KDIGO 2024 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Apr 2024 [internet publication].
https://kdigo.org/guidelines/ckd-evaluation-and-management
Urine albumin measurement is an important component in screening for CKD. The presence of proteinuria is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease, end-stage renal disease, stroke and death in the general population, and in patients with CKD.[4]Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium; Matsushita K, van der Velde M, Astor BC, et al. Association of estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in general population cohorts: a collaborative meta-analysis. Lancet. 2010 Jun 12;375(9731):2073-81.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20483451?tool=bestpractice.com
[5]Astor BC, Matsushita K, Gansevoort RT, et al. Lower estimated glomerular filtration rate and higher albuminuria are associated with mortality and end-stage renal disease. A collaborative meta-analysis of kidney disease population cohorts. Kidney Int. 2011 Jun;79(12):1331-40.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21289598?tool=bestpractice.com
[6]van der Velde M, Matsushita K, Coresh J, et al. Lower estimated glomerular filtration rate and higher albuminuria are associated with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. A collaborative meta-analysis of high-risk population cohorts. Kidney Int. 2011 Jun;79(12):1341-52.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21307840?tool=bestpractice.com
[7]Gansevoort RT, Matsushita K, van der Velde M, et al. Lower estimated GFR and higher albuminuria are associated with adverse kidney outcomes. A collaborative meta-analysis of general and high-risk population cohorts. Kidney Int. 2011 Jul;80(1):93-104.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21289597?tool=bestpractice.com
[8]British Medical Journal. Low eGFR and high albuminuria predict end stage kidney disease and death at all ages. BMJ. 2012 Nov 7;345:e7478.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23135200?tool=bestpractice.com
[9]Harrison TG, Tam-Tham H, Hemmelgarn BR, et al. Change in proteinuria or albuminuria as a surrogate for cardiovascular and other major clinical outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Can J Cardiol. 2019 Jan;35(1):77-91.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30595186?tool=bestpractice.com
[10]Huang R, Chen X. Increased spot urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio and stroke incidence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019 Oct;28(10):104260.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31350166?tool=bestpractice.com
Presence of proteinuria is associated with a higher mortality in critically ill patients; the degree of proteinuria post renal transplantation is predictive of graft and patient survival.[11]Han SS, Ahn SY, Ryu J, et al. Proteinuria and hematuria are associated with acute kidney injury and mortality in critically ill patients: a retrospective observational study. BMC Nephrol. 2014 Jun 18;15:93.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4072664
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24942179?tool=bestpractice.com
[12]Lin LY, Jenq CC, Liu CS, et al. Proteinuria can predict short-term prognosis in critically ill cirrhotic patients. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2014 Apr;48(4):377-82.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24440941?tool=bestpractice.com
[13]Borrego J, Mazuecos A, Gentil MA, et al. Proteinuria as a predictive factor in the evolution of kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2013;45(10):3627-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24314978?tool=bestpractice.com
Reduction of proteinuria by pharmacologic therapy is used as a surrogate marker in the management of CKD and many acute glomerular diseases, and is associated with improved renal outcomes.[14]Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Bain RP, et al. The effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition on diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 1993 Nov 11;329(20):1456-62.
http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJM199311113292004#t=article
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8413456?tool=bestpractice.com
[15]The GISEN Group. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of effect of ramipril on decline in glomerular filtration rate and risk of terminal renal failure in proteinuric, non-diabetic nephropathy. Lancet. 1997 Jun 28;349(9069):1857-63.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9217756?tool=bestpractice.com
[16]Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, et al. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2001 Sep 20;345(12):861-9.
http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa011161#t=article
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11565518?tool=bestpractice.com
[17]Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Clarke WR, et al. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2001 Sep 20;345(12):851-60.
http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa011303#t=article
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11565517?tool=bestpractice.com
[18]Parving HH, Lehnert H, Bröchner-Mortensen J, et al; Irbesartan in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Microalbuminuria Study Group. The effect of irbesartan on the development of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2001 Sep 20;345(12):870-8.
http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa011489#t=article
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11565519?tool=bestpractice.com
[19]Wright JT Jr, Bakris G, Greene T, et al. Effect of blood pressure lowering and antihypertensive drug class on progression of hypertensive kidney disease: results from the AASK trial. JAMA. 2002 Nov 20;288(19):2421-31.
http://jama.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/full/288/19/2421
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12435255?tool=bestpractice.com
[20]Inker LA, Levey AS, Pandya K, et al. Early change in proteinuria as a surrogate end point for kidney disease progression: an individual patient meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014 Jul;64(1):74-85.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24787763?tool=bestpractice.com
[21]Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Glomerular Diseases Work Group. KDIGO 2021 clinical practice guideline for the management of glomerular diseases. Kidney Int. 2021 Oct;100(4s):S1-276.
https://www.kidney-international.org/article/S0085-2538(21)00562-7/fulltext
Proteinuria definitions
Total urine protein or just the albumin fraction can be measured. Urine albumin measurements are better validated in regard to association with risk for CKD progression and cardiovascular events.
Albuminuria
Albuminuria is graded as follows:[3]Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes. KDIGO 2024 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Apr 2024 [internet publication].
https://kdigo.org/guidelines/ckd-evaluation-and-management
A1 (normal to mildly increased albuminuria)
A2 (moderately increased albuminuria)
A3 (severely increased albuminuria)
Nephrotic-range proteinuria
Glomerular proteinuria
Tubular proteinuria
Passage of low molecular weight proteins (e.g., retinol-binding protein, alpha-2-microglobulin, beta-2-microglobulin) into the urine.
Overflow proteinuria
Urine total protein: up to 20 g/day.
Overproduction of small proteins (e.g., myoglobin, light chains) leads to increased glomerular filtration and appearance in the urine.
Epidemiology
Proteinuria is common, and prevalence increases with kidney disease progression. There is evidence that both moderately and severely increased albuminuria is more common in black people than in white people.[22]Afkarian M, Zelnick LR, Hall YN, et al. Clinical manifestations of kidney disease among US adults with diabetes, 1988-2014. JAMA. 2016 Aug 9;316(6):602-10.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5444809
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27532915?tool=bestpractice.com
As the GFR declines from >90 mL/minute/1.73 m² to 15-59 mL/minute/1.73 m², the prevalence of moderately increased albuminuria (ACR <300 mg/g) increases from 6.0% to 23.2%, and the prevalence of severely increased albuminuria (ACR ≥300 mg/g) increases from 0.6% to 8.6%.[23]Astor BC, Hallan SI, Miller ER 3rd, et al. Glomerular filtration rate, albuminuria, and risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in the US population. Am J Epidemiol. 2008 May 15;167(10):1226-34.
http://aje.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/full/167/10/1226
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18385206?tool=bestpractice.com
Effect of albuminuria on prognosis of chronic kidney disease
Albuminuria is an independent risk factor for the progression of CKD.[24]McFarlane P, Cherney D, Gilbert RE, et al. Diabetes Canada 2018 clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and management of diabetes in Canada: chronic kidney disease in diabetes. Can J Diabetes 2018;42(Suppl 1):S201-S209.
http://guidelines.diabetes.ca/cpg/chapter29
Severely increased levels of albuminuria in the setting of normal GFR may impart a greater risk for progressive CKD than mildly reduced GFR with normoalbuminuria. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Prognosis of CKD by GFR and albuminuria category: CKD, chronic kidney disease; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; KDIGO, Kidney Disease Improving Global OutcomesReprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Kidney International Supplements (vol 3, issue 1, January 2013), copyright 2013 [Citation ends].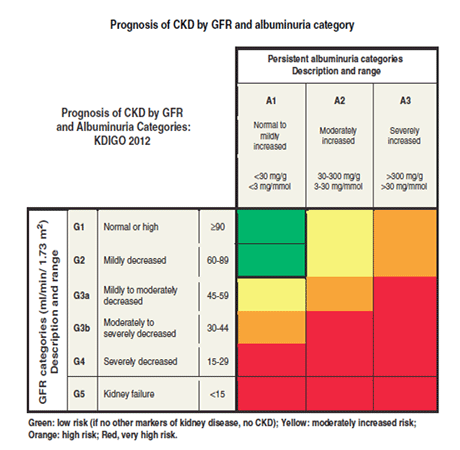
In patients with advanced CKD, proteinuria is the strongest predictor of time to end-stage renal disease.[25]Raman M, Green D, Middleton RJ, et al. Older people with chronic kidney disease: definition, and influence of biomarkers and medications upon cardiovascular and renal outcomes. J Ren Care. 2016 Sep;42(3):150-61.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27364740?tool=bestpractice.com
[26]Grams ME, Li L, Greene TH, et al. Estimating time to ESRD using kidney failure risk equations: results from the African American Study of Kidney Disease and Hypertension (AASK). Am J Kidney Dis. 2015 Mar;65(3):394-402.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25441435?tool=bestpractice.com
Moreover, changes in ACR correlate with the risk of developing end-stage renal disease.[27]Coresh J, Heerspink HJL, Sang Y, et al. Change in albuminuria and subsequent risk of end-stage kidney disease: an individual participant-level consortium meta-analysis of observational studies. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019 Feb;7(2):115-127.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6379893
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30635225?tool=bestpractice.com
[28]Heerspink HJL, Greene T, Tighiouart H, et al. Change in albuminuria as a surrogate endpoint for progression of kidney disease: a meta-analysis of treatment effects in randomised clinical trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019 Feb;7(2):128-139.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30635226?tool=bestpractice.com

Log in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
