Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- adolescent and young adult age
- history of living in area of high temperature and humidity
- susceptible skin characteristics
- positive drug history
- lack of pruritus or pain
- dyspigmentation
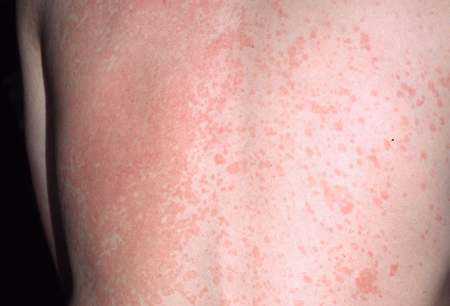
- macules or patches
- seborrheic distribution
- fine overlying scale
Other diagnostic factors
- yellow fluorescence under Wood lamp exam
Risk factors
- high ambient temperature and humidity
- adolescent and young adult age
- hyperhidrosis
- systemic corticosteroid or other immunosuppressant use
- participation in athletics
- greasy skin
- family history of PV
- malnutrition
- use of oral contraceptives
- HIV infection and other immunosuppressive conditions
- use of occlusive ointments or creams
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- microscopic exam with potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation
Investigations to consider
- skin biopsy
- culture
- Gram stain
Treatment algorithm
nonpregnant
pregnant
recurrent disease after successful pathogen eradication
Contributors
Authors
Brian L. Swick, MD

Clinical Professor
Departments of Dermatology and Pathology
University of Iowa
Iowa City
IA
Disclosures
BLS declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Nnenna Agim, MD, FAAD
Associate Professor of Dermatology
University of Texas Southwestern
Dallas
TX
Disclosures
NA declares that she has no competing interests.
Helen Goodyear, MBChB, MRCP, FRCPCH, MD, MMed
Consultant Paediatrician
Heartlands Hospital
Birmingham
UK
Disclosures
HG declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Schwartz RA. Superficial fungal infections. Lancet. 2004 Sep 25-Oct 1;364(9440):1173-82. Abstract
Gupta AK, Bluhm R, Summerbell R. Pityriasis versicolor. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2002 Jan;16(1):19-33. Abstract
Drake LA, Dinehart SM, Farmer ER, et al. Guidelines of care for superficial mycotic infections of the skin: pityriasis (tinea) versicolor. Guidelines/Outcomes Committee. American Academy of Dermatology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996 Feb;34(2 Pt 1):287-9.
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Vitiligo
- Tinea corporis
- Seborrheic dermatitis
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Guidelines of care for superficial mycotic infections of the skin: pityriasis (tinea) versicolor
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer
