Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- nonspecific prodrome
- severe neurologic symptoms (coma, focal abnormalities, seizures)
- mild neurologic symptoms (headache, confusion)
- fever
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- age 30 to 50 years
- digestive symptoms (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain)
- weakness
- bleeding symptoms (purpura, ecchymosis, menorrhagia)
Fatores de risco
- black ethnicity
- female gender
- obesity
- pregnancy (near term or postpartum period)
- cancer therapies
- HIV infection
- bone marrow transplantation
- antiplatelet agents
- quinine
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- platelet count
- hemoglobin
- haptoglobin
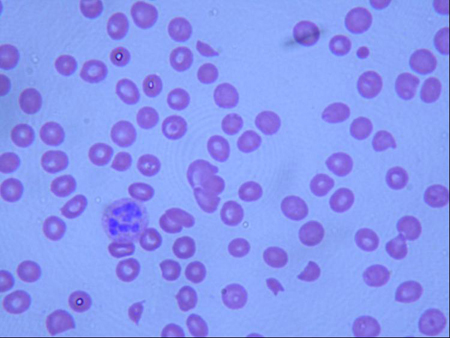
- peripheral smear
- reticulocyte count
- urinalysis
- BUN and creatinine
- direct Coombs test
Investigações a serem consideradas
- ADAMTS-13 activity assay and inhibitor titers
Algoritmo de tratamento
acquired (idiopathic) TTP: acute episode
acquired (idiopathic) TTP: following resolution of acute episode
Colaboradores
Autores
Sandeep K. Rajan, MD
Associate Professor of Medicine
Division of Hematology and Medical Oncology
Vanderbilt University
Nashville
Tennessee
Declarações
SKR has received honoraria for advisory consultancy and speakers bureau, and received research funds from Alexion, Novo-Nordisk, Sanofi and Appelis.
Agradecimentos
Dr Sandeep K. Rajan would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Rebecca Fischer Connor, a previous contributor to this topic.
Declarações
RFC declares that she has no competing interests.
Revisores
James N. George, MD
George Lynn Cross Professor
Department of Biostatistics and Epidemiology
University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center
Oklahoma City
OK
Declarações
JNG declares that he has no competing interests.
Christoph Pechlaner, MD
Associate Professor of Medicine
Department of Internal Medicine
Innsbruck Medical University
Innsbruck
Austria
Declarações
CP declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Scully M, Cataland S, Coppo P, et al. Consensus on the standardization of terminology in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and related thrombotic microangiopathies. J Thromb Haemost. 2017 Feb;15(2):312-22.Texto completo Resumo
Scully M, Hunt BJ, Benjamin S, et al. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and other thrombotic microangiopathies. Br J Haematol. 2012 Aug;158(3):323-35.Texto completo Resumo
Terrell DR, Williams LA, Vesely SK, et al. The incidence of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome: all patients, idiopathic patients, and patients with severe ADAMTS-13 deficiency. J Thromb Haemost. 2005 Jul;3(7):1432-6.Texto completo Resumo
Moschowitz E. An acute febrile pleiochromic anemia with hyaline thrombosis of the terminal arterioles and capillaries. Arch Intern Med. 1925;36:89.
Moore JC, Hayward CP, Warkentin TE, et al. Decreased von Willebrand factor protease activity associated with thrombocytopenic disorders. Blood. 2001;98:1842-1846.Texto completo Resumo
Banno F, Kokame K, Okuda T, et al. Complete deficiency in ADAMTS13 is prothrombotic, but it alone is not sufficient to cause thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2006 Apr 15;107(8):3161-6.Texto completo Resumo
Veyradier A, Meyer D. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and its diagnosis. J Thromb Haemost. 2005 Nov;3(11):2420-7. Resumo
Rock GA, Shumak KH, Buskard NA, et al. Comparison of plasma exchange with plasma infusion in the treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Canadian Apheresis Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1991 Aug 8;325(6):393-7. Resumo
Cuker A, Cataland SR, Coppo P, et al. Redefining outcomes in immune TTP: an international working group consensus report. Blood. 2021 Apr 8;137(14):1855-61.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)
- Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS)
- Hypertension, malignant
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- ISTH guidelines for the diagnosis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
- Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and other thrombotic microangiopathies
Mais DiretrizesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal