Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- hypercyanotic episodes
- harsh systolic ejection murmur
- cyanosis
- tachypnea
Other diagnostic factors
- shock
Risk factors
- trisomy 21, 18, or 13
- chromosome 22q11 deletions (DiGeorge syndrome)
- Jagged1 gene mutations (Alagille syndrome)
- mutation in NKX2.5 gene
- environmental factors
- family history of congenital heart disease
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- pulse oximetry
- echocardiogram
- ECG
- CXR
- hyperoxygenation test
Tests to consider
- cardiac CT angiography or MRI
- cardiac catheterization
Treatment algorithm
hypercyanotic spells
neonate with profound cyanosis and severely limited pulmonary blood flow
neonate or infant with nonremitting severe cyanosis
all patients
Contributors
Authors
Jeffrey Gossett, MD

Vice President and System Chief of Pediatric Cardiology
Professor of Pediatrics
Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Cohen Children’s Medical Center, Northwell Health
New Hyde Park
NY
Disclosures
JG declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Jeffrey Gossett would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Anna Kamp, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
AK declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Adam B. Christopher, MD
Assistant Professor of Pediatrics
Director of Cardiac MRI
UPMC Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh
PA
Disclosures
ABC declares that he has no competing interests.
Ranjit Aiyagari, MD
Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics
University of Michigan
Ann Arbor
MI
Disclosures
RA declares that he has no competing interests.
Michael Cheung, BSc, MBChB, MD
Deputy Director
Department of Cardiology
Royal Children's Hospital
Melbourne
Australia
Disclosures
MC declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Valente AM, Cook S, Festa P, et al. Multimodality imaging guidelines for patients with repaired tetralogy of Fallot: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography: developed in collaboration with the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance and the Society for Pediatric Radiology. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2014 Feb;27(2):111-41. Abstract
Hirsch JC, Mosca RS, Bove EL. Complete repair of tetralogy of Fallot in the neonate: results in the modern era. Ann Surg. 2000 Oct;232(4):508-14.Full text Abstract
Habib G, Lancellotti P, Antunes MJ, et al. 2015 ESC guidelines for the management of infective endocarditis. Eur Heart J. 2015 Nov 21;36(44):3075-128.Full text Abstract
Stout KK, Daniels CJ, Aboulhosn JA, et al. 2018 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of adults with congenital heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation. 2019 Apr 2;139(14):e698-800.Full text Abstract
Lui GK, Saidi A, Bhatt AB, et al. Diagnosis and management of noncardiac complications in adults with congenital heart disease: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017 Nov 14;136(20):e348-92.Full text Abstract
Baumgartner H, De Backer J, Babu-Narayan SV, et al. 2020 ESC guidelines for the management of adult congenital heart disease. Eur Heart J. 2021 Feb 11;42(6):563-645.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
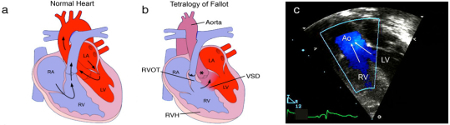
Differentials
- Other cyanotic congenital cardiac abnormalities
- Pulmonary stenosis
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- ACR Appropriateness Criteria: congenital or acquired heart disease
- Recommendations for the adult cardiac sonographer performing echocardiography to screen for critical congenital heart disease in the newborn
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer