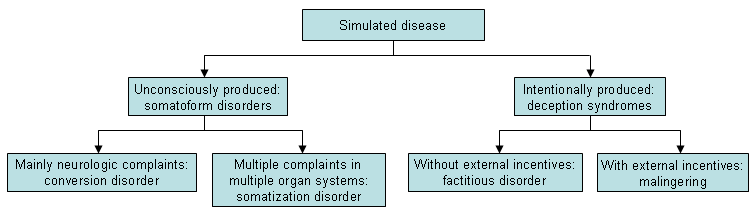
შეჯამება
განსაზღვრება
ანამნეზი და გასინჯვა
ძირითადი დიაგნოსტიკური ფაქტორები
- history of unexplained complaints or inconsistency over time
- unusual presentation relative to demographics
სხვა დიაგნოსტიკური ფაქტორები
- symptoms more exaggerated while aware of being observed
- presentation for care at many different hospitals
- eyewitness evidence of the patient manipulating findings
- dramatic history of travel and acute illness (Munchausen subtype)
- multiple abdominal scars (Munchausen subtype)
- medications or medical paraphernalia found in an unusual location in a patient's room
რისკფაქტორები
- female sex (factitious disorder)
- medically related employment (factitious disorder)
- cluster B personality characteristics (factitious disorder)
- male sex (Munchausen subtype)
- single marital status (Munchausen subtype)
- age 40 to 50 years (Munchausen subtype)
- antisocial personality traits (Munchausen subtype)
დიაგნოსტიკური კვლევები
1-ად შესაკვეთი გამოკვლევები
- clinical history and exam
გასათვალისწინებელი კვლევები
- cultures (e.g., blood or wound)
- serum C-peptide
- urine sulfonylureas
- urine electrolytes
- urine protein
- serum thyroglobulin
მკურნალობის ალგორითმი
suspected factitious disorder
კონტრიბუტორები
ავტორები
James L. Levenson, MD
Professor of Psychiatry
Internal Medicine and Surgery
Vice-Chair
Department of Psychiatry
Chair
Division of Consultation/Liaison Psychiatry
Virginia Commonwealth University
Richmond
VA
გაფრთხილება:
JLL is the author of a reference cited in this topic.
მადლიერება
Prof Levenson would like to gratefully acknowledge Prof Christopher P. Kogut, a previous contributor to this topic.
გაფრთხილება:
CPK declares that he has no competing interests.
რეცენზენტები
Tanveer Padder,
Consulting Psychiatrist
Padder Health Services
Laurel
MD
გაფრთხილება:
TP declares that he has no competing interests.
Marc Feldman,
Clinical Professor of Psychiatry
University of Alabama
Tuscaloosa
AL
Declarações
MF receives royalties for two books on the subjects covered in this topic (Routledge publishing and American Psychiatric Publishing). He is also an author of references cited in this topic.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th ed., text revision (DSM-5-TR). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2022.
Asher R. Munchausen's syndrome. Lancet. 1951 Feb 10;1(6650):339-41. Resumo
Ford CV, Sonnier L, & McCullumsmith C. Chapter 12: Deception syndromes. In: Levenson JL, ed. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of psychosomatic medicine and consultation-liaison psychiatry. 3rd ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2018.
Sutherland AJ, Rodin GM. Factitious disorders in a general hospital setting: clinical features and a review of the literature. Psychosomatics. 1990 Fall;31(4):392-9. Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Malingering
- Somatic symptom and related disorders
- Organic disease
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Assessment and management of adults and children in cases of fabricated or induced illness
- Munchausen by proxy: clinical and case management guidance
Mais DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Factitious disorders
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal