Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- diplopia
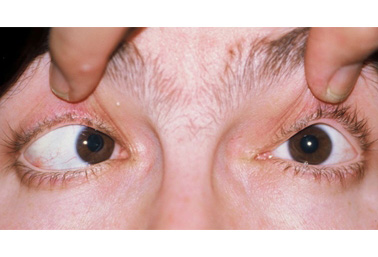
- eye misalignment
- amblyopia
Other diagnostic factors
- abnormal eye movements
- visual confusion
- asthenopia
- intermittent closure of one eye
- cranial nerve palsy
Risk factors
- family history of strabismus
- prematurity
- low birth weight
- maternal smoking during pregnancy
- refractive error
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- cover test
- simultaneous prism and cover test (SPCT)
- uncover test (UCT)
- alternate prism cover test (APCT)
- Hirschberg test
- Krimsky test
Tests to consider
- version testing
- duction testing
- forced duction testing
- CT or MRI of orbit
- MRI of brain
- CT chest
Treatment algorithm
primary strabismus
secondary strabismus
Contributors
Authors
Daniel J. Salchow, MD

Director
Pediatric Ophthalmology; Strabismus; Neuro-ophthalmology
Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin
Berlin
Germany
Disclosures
DJS declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Donny W. Suh, MD, FAAP, MBA, FACS
Chief and Professor of Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus
Department of Ophthalmology
University of California, Irvine
Irvine
CA
Disclosures
DWS declares that he has no competing interests.
Peter Tiffin, BMedSci(Hons), MBBS, FRCOphth
Ophthalmology Consultant
City Hospitals Sunderland
Sunderland
UK
Disclosures
PT declares that he has no competing interests.
Jonathan Smith, MBBS, MRCP, MRCOphth
Specialist Registrar in Ophthalmology
Ophthalmics
Royal Victoria Infirmary
Newcastle
UK
Disclosures
JS declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
US Preventive Services Task Force. Vision in children ages 6 months to 5 years: screening. Sep 2017 [internet publication].Full text
Sprunger DT, Lambert SR, Hercinovic A, et al. Esotropia and exotropia preferred practice pattern®. Ophthalmology. 2023 Mar;130(3):P179-221.Full text Abstract
Hutchinson AK, Morse CL, Hercinovic A, et al. Pediatric eye evaluations preferred practice pattern. Ophthalmology. 2023 Mar;130(3):P222-70.Full text Abstract
Dagi LR, Velez FG, Holmes JM, et al. Adult strabismus preferred practice pattern®. Ophthalmology. 2024 Apr;131(4):P306-403.Full text
Cruz OA, Repka MX, Hercinovic A, et al. Amblyopia preferred practice pattern. Ophthalmology. 2023 Mar;130(3):P136-78.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Pseudostrabismus
- Blurred vision
- Monocular diplopia
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Adult strabismus summary benchmarks
- Adult strabismus summary benchmarks
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer