Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- watery discharge
- ropy, mucoid discharge
- purulent discharge
- itching predominant symptom
- red eye
- eyelids stuck together in morning
- tender, preauricular lymphadenopathy
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- conjunctival follicles
- chemosis
- swollen eyelids
- superficial punctate keratopathy
- unilateral symptoms and signs
- use of drugs that may lead to eye irritation
- contact lens use
- corneal subepithelial infiltrates
- corneal pannus
- vesicular skin rash
- symptoms and signs of related systemic disease
Fatores de risco
- exposure to infected person
- infection in one eye
- environmental irritants
- allergen exposure
- concurrent infection
- camps, swimming pools, military bases
- hot, dry climate
- atopic dermatitis
- contact lens use
- ocular prosthesis
- trauma: mechanical, chemical, or ultraviolet
- recent surgery or exposed sutures
- rosacea
- allogeneic stem cell transplantation
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN)
- prior infection with herpes simplex virus
- in neonate: vaginal delivery
- oculogenital spread
- asthma
- hay fever
- use of topical eye preparations
- use of oral antihistamines or anticholinergic drugs
- neoplasia
- history of rheumatologic disease
- dysthyroid states
- immunocompromised state
- vasculitis
- nasolacrimal duct obstruction
- abnormality of supporting structures of the eye (adnexa)
- severe tear deficiency
- trauma
- use of biologic agents
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- rapid adenovirus immunoassay
Investigações a serem consideradas
- conjunctival cultures
- special stains (Gram, Giemsa)
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
- ocular pH
- allergy skin testing
- tear immunoglobulin E level
Algoritmo de tratamento
allergic conjunctivitis (seasonal/perennial)
bacterial conjunctivitis
chlamydial conjunctivitis (inclusion)
viral conjunctivitis
neonatal conjunctivitis
contact lens related
mechanical conjunctivitis
toxic/chemical conjunctivitis
drug-related conjunctivitis
Colaboradores
Autores
Christopher McStay, MD
Associate Professor of Emergency Medicine
Vice Chair of Clinical Operations
Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons
New York
NY
Declarações
CM declares that he has no competing interests.
Agradecimentos
Dr Christopher McStay would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Lee Raykovicz and Dr Robert Sambursky, previous contributors to this topic.
Declarações
LR declared he was Director of Clinical Relations, Rapid Pathogen Screening, Inc. RS is employed by Verséa Ophthalmics and serves on the board of Visus Therapeutics.
Revisores
Michael Ehrenhaus, MD
Director
Cornea, External Disease & Refractive Surgery
Long Island College Hospital Eye Center
Assistant Professor of Ophthalmology
SUNY Downstate Medical Center
Brooklyn
NY
Declarações
ME declares that he has no competing interests.
Scott Fraser, MD, FRCS (Ed), FRCOphth
Consultant Ophthalmologist
Sunderland Eye Infirmary
Sunderland
UK
Declarações
SF declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Cheung, Albert Y. et al. Conjunctivitis preferred practice pattern. Ophthalmology. 2024 Feb 12;131(4): 134-204.Texto completo
Castillo M, Scott NW, Mustafa MZ, et al. Topical antihistamines and mast cell stabilisers for treating seasonal and perennial allergic conjunctivitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jun 1;(6):CD009566.Texto completo Resumo
Chen YY, Liu SH, Nurmatov U, et al. Antibiotics versus placebo for acute bacterial conjunctivitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Mar 13;3(3):CD001211.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
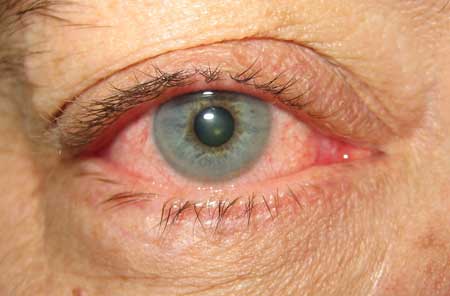
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Dry eyes
- Blepharitis
- Episcleritis
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Conjunctivitis preferred practice pattern
- Cornea/external disease summary benchmarks
Mais DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Conjunctivitis
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal