Summary
Definition
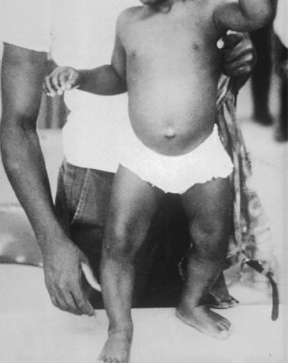
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- history of breast-feeding
- history of inadequate sunlight exposure
- history of calcium deficiency
- history of phosphate deficiency
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- bone pain
- growth faltering
- delayed achievement of motor milestones
- bony deformities
- muscle weakness
- carpopedal spasm
- tetany
- numbness or paresthesias
- hypocalcemic seizures
Fatores de risco
- age 6 to 23 months
- inadequate sunlight exposure
- breast-feeding
- darker skin complexion
- calcium deficiency
- phosphate deficiency
- family history of rickets
- antacids, loop diuretics, corticosteroids, or anticonvulsants
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- radiograph of a long bone
- serum calcium
- serum inorganic phosphorus
- serum parathyroid hormone level
- 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels (calcidiol)
- alkaline phosphatase and liver function tests
- serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen
- urinary calcium and phosphorus
Investigações a serem consideradas
- 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D levels (calcitriol)
Algoritmo de tratamento
symptomatic hypocalcemia
calcium-deficient rickets: vitamin D deficiency
calcium-deficient rickets: calcium deficiency
calcium-deficient rickets: pseudovitamin D deficiency
calcium-deficient rickets: vitamin D resistance
hypophosphatemic rickets: X-linked
hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria
hypophosphatemic rickets: tumor-induced
Colaboradores
Autores
Carlos Palacio, MD, MPH, FACP

Professor of Medicine
Associate Program Director
Internal Medicine Residency
Department of Medicine
University of Florida College of Medicine
Jacksonville
FL
Declarações
CP declares that he has no competing interests.
Firas Warda, MD
Endocrinology Fellow
Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism
Department of Medicine
University of Florida College of Medicine
Jacksonville
FL
Declarações
FW declares that he has no competing interests.
Agradecimentos
Professor Carols Palacio and Dr Firas Warda would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Robert Olney, a previous contributor to this topic.
Declarações
RO declares that he has no competing interests.
Revisores
Phil Fischer, MD
Professor of Pediatrics
Mayo Clinic
Rochester
MN
Declarações
PF declares that he has no competing interests.
Zulf Mughal, MD
Consultant in Paediatric Bone Disorders
Department of Paediatric Endocrinology
Royal Manchester Children's Hospital
UK
Declarações
No disclosures
Arshag Mooradian, MD
Professor of Medicine
University of Florida College of Medicine
Jacksonville
FL
Declarações
AM declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG committee opinion no. 495: vitamin D: screening and supplementation during pregnancy. Jul 2011 [internet publication].Texto completo
Munns CF, Shaw N, Kiely M, et al. Global consensus recommendations on prevention and management of nutritional rickets. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Feb;101(2):394-415.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Hypophosphatasia
- Metaphyseal dysostoses
- Blount syndrome
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Rickets: standard treatment guidelines
- Global consensus recommendations on prevention and management of nutritional rickets
Mais DiretrizesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal