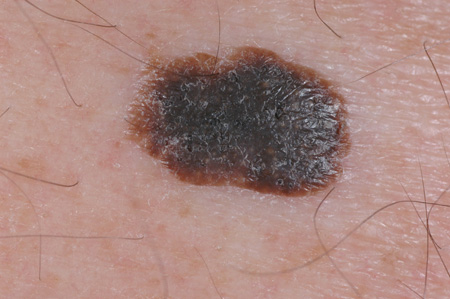
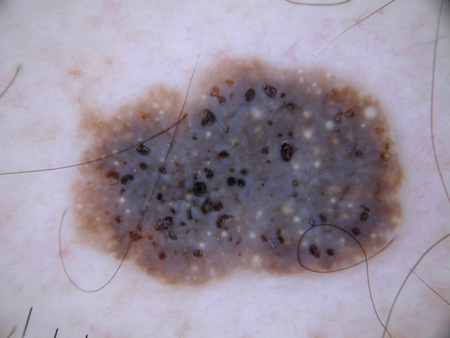
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
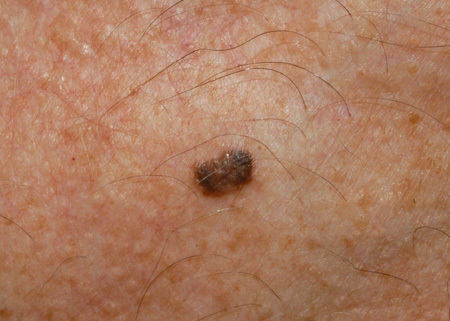
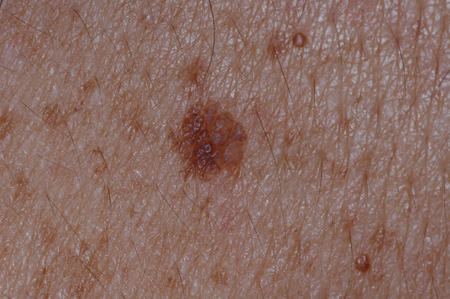
- lesions appear "stuck-on"
- localization on torso or face
- yellow or light- to dark-brown-colored lesions
- slightly raised, flat surface lesions
- wart-like texture
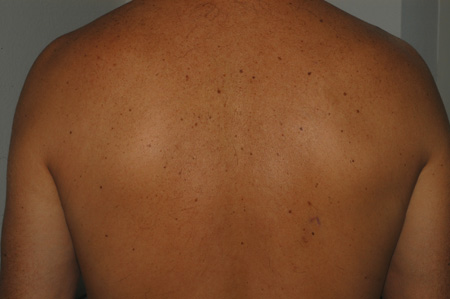
- multiple lesions
- painless
- itching (prurigo)
Other diagnostic factors
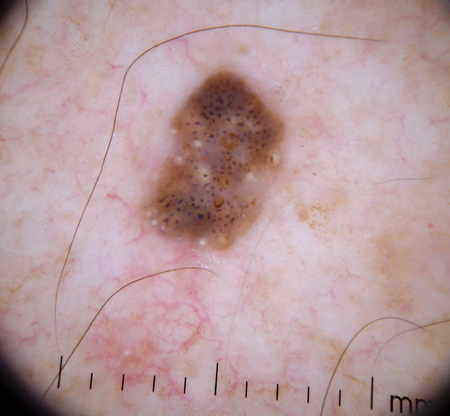
- round yellow-white horn pearls in the surface of lesions
Risk factors
- age over 50 years
- Fitzpatrick skin type I or II
- Fitzpatrick skin type IV, V, or VI (dermatosis papulosa nigra)
- female sex (dermatosis papulosa nigra)
- family history
- sun/UV exposure
- pregnancy
Diagnostic tests
Tests to consider
- dermoscopy
- biopsy and histopathologic examination
- reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM)
Treatment algorithm
irritated or itching lesions
raised seborrheic keratosis
flat seborrheic keratosis
Contributors
Authors
Ralph Braun, MD
Professor
Clinic Utoquai
Zurich
Switzerland
Disclosures
RB declares that he has no competing interests.
Isabel Kolm-Djamei, MD
Consultant Dermatologist
Department of Pathology
Cantonal Hospital Lucerne
Lucerne
Switzerland
Disclosures
IKD declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Erin Warshaw, MD, MS
Associate Professor
Department of Dermatology
University of Minnesota
MN
Disclosures
EW declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Seaton E, Madan V. Benign keratinocytic acanthomas and proliferations. In: Barker J, Griffiths C, Bleiker T, eds. Rook's textbook of dermatology. 10th ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2024.
Patterson JW. Chapter 32: Tumors of the epidermis. In: Patterson JW. Weedon's skin pathology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025: 877-936.
Barthelmann S, Butsch F, Lang BM, et al. Seborrheic keratosis. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2023 Mar;21(3):265-77.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.

Differentials
- Malignant melanoma
- Viral warts
- Nevus
More DifferentialsLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer