Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- pruritus
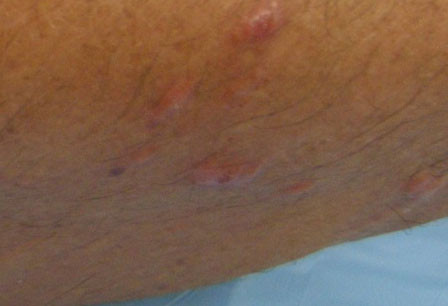
- blisters and vesicles
- weeping, oozing, and crusting
Other diagnostic factors
- previous exposure
- breathing difficulties
- generalized erythroderma
- periorbital edema
- systemic contact dermatitis
- black-spot dermatitis
Risk factors
- occupation that involves exposure to relevant plants
- outdoor activities
- domestic pets and livestock
- use of forestry equipment and machinery
- smoke from burning Toxicodendron species
- previous exposure or allergy to relevant plants
- children
- genetic susceptibility
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- clinical diagnosis
Tests to consider
- botanical identification
- black-spot test
- CBC
Emerging tests
- patch test
Treatment algorithm
immediate treatment postexposure
mild dermatitis
moderate dermatitis
severe dermatitis
chronic severe dermatitis from repeated exposure
Contributors
Authors
Marius Rademaker, BM FRCP, FRACP DM, FNZDSI, FACD
Clinical Trials New Zealand
Waikato Hospital Campus
Hamilton
New Zealand
Disclosures
MR declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Brian Swick, MD
Clinical Assistant Professor
University of Iowa College of Medicine
Iowa City
IA
Disclosures
BS declares that he has no competing interests.
Christopher Lovell, MBBS
Consultant Dermatologist
Kinghorn Dermatology Unit
Royal United Hospital
Bath
UK
Disclosures
CL declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Guin JD, Beaman JH, Baer H. Toxic anacardiaceae. In: Avalos J, Maibach HI, eds. Dermatologic botany. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 1999.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Poisonous plants and work. Aug 2024 [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Phytodermatitis
- Phytophotodermatitis
- Allergic contact dermatitis
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Poisonous plants and work
- Establishing consensus on the treatment of
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer