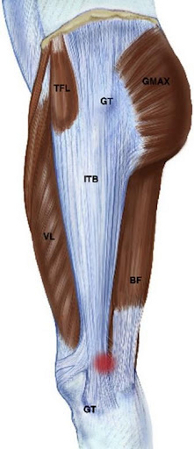
Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- history of athleticism
- sharp or burning pain superior to the lateral joint line
- positive Noble test
- positive Ober test
- positive modified Thomas test
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- reduced hip abductor muscle strength
- genu varum (bow leg), hindfoot and forefoot varum, and pes cavus (high arch)
- prominent lateral femoral epicondyle
- swelling, local edema, or crepitations
Fatores de risco
- athlete
- high weekly mileage
- interval training
- muscular weakness of knee extensors, knee flexors, and hip abductors
- lack of running experience
- use of worn-out running shoes
- downhill running, or running on a cambered or slippery surface
- female sex
- preexisting iliotibial band tightness
- leg-length discrepancies
- step width and strain rate
- knee varus in male runners
- muscular weakness in hip external rotator muscles in male runners
- excessive hip internal rotation in male runners
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- clinical diagnosis
Investigações a serem consideradas
- x-ray of knee
- ultrasound of knee
- MRI of knee
Algoritmo de tratamento
pain and inflammation
resolved pain and inflammation
refractory to conservative treatment
Colaboradores
Autores
Bob Baker, PT, PhD, MBA, OCS

Rehabilitation Services Manager
NorthBay Healthcare
Fairfield
CA
Declarações
BB is an author of articles cited in this topic.
Jenson C. Mak, PhD, FRACP, FAFRM, FACP, MBBS

Rehabilitation Fellow
University of Sydney
Sydney
Australia
Declarações
JCM declares that he has no competing interests.
Michael Fredericson, MD, FACSM

Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery
Stanford Medical Center
Stanford University
Stanford
CA
Declarações
MF is an author of several articles cited in this topic.
Revisores
Robert Werner, MD
Professor
Chief of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
Ann Arbor VA Medical Center
Ann Arbor
MI
Declarações
RW has been reimbursed by the University of Michigan for attending several conferences and has been paid an honorarium for speaking at the American Association of Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Medicine national meeting. RW has been paid by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, the American Dental Association, and SmartHealth as a consultant and has received grant funding from the UAW/GM Health and Safety Board (over US$1 million).
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Fredericson M, Weir A. Practical management of iliotibial band friction syndrome in runners. Clin J Sport Med. 2006 May;16(3):261-8. Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Biceps femoris tendinopathy
- Degenerative joint disease
- Lateral collateral ligament (LCL) sprain
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Practical management of iliotibial band friction syndrome in runners
Mais DiretrizesVideos
Knee exam
Mais vídeosConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal