Summary
Definición
Anamnesis y examen
Principales factores de diagnóstico
- presence of polytrauma/multiple injury
- paralysis of shoulder
- paralysis of bicep
- numbness of radial digits of hand and shoulder
- paralysis of triceps
- paralysis of wrist/finger extensors
- flail/insensate extremity
- absent tendon reflexes
Factores de riesgo
- motor vehicle accident
- neurofibromatosis
- improper positioning during surgery
- age <50 years
- male sex
- Parsonage-Turner syndrome
- tumors (primary and metastatic tumors)
- rib abnormalities
- metabolic disorders
Pruebas diagnósticas
Primeras pruebas diagnósticas para solicitar
- Electromyography
Pruebas diagnósticas que deben considerarse
- MRI
- CT/myelography
Pruebas emergentes
- Ultrasound
Algoritmo de tratamiento
upper (C5-6) with or without middle (C7) root injury
isolated lower root (C8-T1) injury
total root avulsion (C5-T1) injury
Colaboradores
Autores
Rahul K. Nath, MD

Director
Texas Nerve and Paralysis Institute
Houston
TX
Divulgaciones
RKN is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Revisores por pares
Abdelouahed Amrani, MD
Professor
Children's Hospital
Rabat
Morocco
Divulgaciones
AA declares that he has no competing interests.
S. Raja Sabapathy, MS, MCh, DNB, FRCS, MAMS
Director and Head
Department of Plastic, Hand and Reconstructive Microsurgery and Burns
Ganga Hospital
Coimbatore
India
Divulgaciones
SRS declares that he has no competing interests.
Agradecimiento de los revisores por pares
Los temas de BMJ Best Practice se actualizan de forma continua de acuerdo con los desarrollos en la evidencia y en las guías. Los revisores por pares listados aquí han revisado el contenido al menos una vez durante la historia del tema.
Divulgaciones
Las afiliaciones y divulgaciones de los revisores por pares se refieren al momento de la revisión.
Referencias
Artículos principales
Nath RK, Lyons AB, Bietz G. Physiological and clinical advantages of median nerve fascicle transfer to the musculocutaneous nerve following brachial plexus root avulsion injury. J Neurosurg. 2006;105:1-5. Resumen
American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: plexopathy. 2021 [internet publication].Texto completo
Artículos de referencia
Una lista completa de las fuentes a las que se hace referencia en este tema está disponible para los usuarios con acceso a todo BMJ Best Practice.
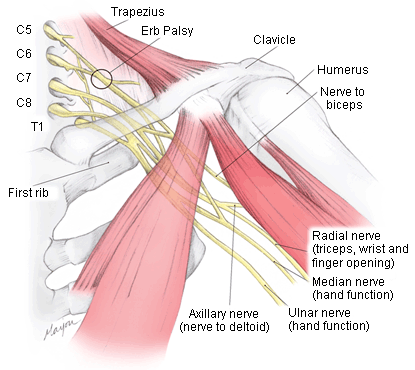
Diferenciales
- Functional or psychogenic weakness (e.g., unilateral loss of motor function or psychogenic parkinsonism)
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- Brain or spinal cord injury
Más DiferencialesGuías de práctica clínica
- ACR appropriateness criteria: plexopathy
Más Guías de práctica clínicaFolletos para el paciente
Rotator cuff injury
Whiplash
Más Folletos para el pacienteInicie sesión o suscríbase para acceder a todo el BMJ Best Practice
El uso de este contenido está sujeto a nuestra cláusula de exención de responsabilidad