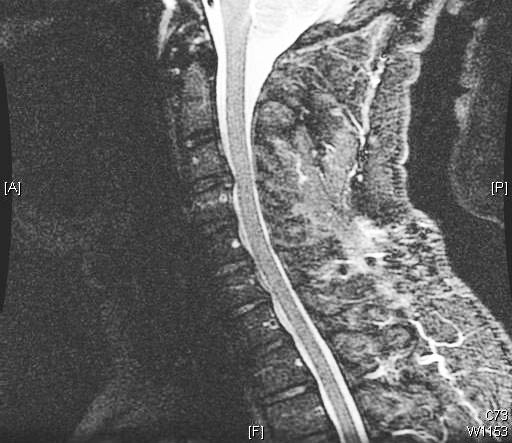
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- spontaneous onset of neck pain
- cervical muscle pain and spasm
- headaches or occipital pain
- weakness or numbness
- presence of radiating shoulder and upper extremity pain
- reflex changes
- proximal arm weakness
- distal hand weakness
- gait ataxia
Other diagnostic factors
- cervical muscle spasm
- decreased cervical range of motion
- sensory changes
Risk factors
- age >50 years
- head or neck trauma
- previous cervical spine surgery
- genetic predisposition
- smoking
- participation in contact sports
- occupation
- heavy load bearing
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- cervical MRI
- cervical x-ray
Tests to avoid
- dermatomal somatosensory evoked potentials (SEPs)
Tests to consider
- cervical CT scan
- cervical CT myelogram
- cervical/upper extremity electrodiagnostic testing
- cervical nerve root block
Treatment algorithm
axial neck pain
cervical spondylotic radiculopathy (CSR)
degenerative cervical myelopathy (DCM)
Contributors
Authors
Dennis A. Turner, MA, MD

Professor
Neurosurgery, Neurobiology, and Biomedical Engineering
Duke University Medical Center
Durham
NC
Disclosures
DAT is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Richard G. Chang, MD, MPH, FAAPMR
Associate Program Director
Sports Fellowship
Assistant Professor
Icahn School of Medicine
Mount Sinai
NY
Disclosures
RGC is a member of the AAPM&R Health Policy & Legislative Committee, and receives reimbursement for travel to in person once a year Capitol Hill meeting and annual AMA State Advocacy Summit conference.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Artículos principales
Bono CM, Ghiselli G, Gilbert TJ, et al; North American Spine Society. An evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of cervical radiculopathy from degenerative disorders. Spine J. 2011 Jan;11(1):64-72. Resumen
Joint Section on Disorders of the Spine and Peripheral Nerves of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons and Congress of Neurological Surgeons. Guidelines for the surgical management of cervical degenerative disease. 2009 [internet publication].Texto completo
American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: cervical neck pain or cervical radiculopathy. 2024 [internet publication].Texto completo
Nikolaidis I, Fouyas IP, Sandercock PA, et al. Surgery for cervical radiculopathy or myelopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Jan 20;(1):CD001466.Texto completo Resumen
Artículos de referencia
Una lista completa de las fuentes a las que se hace referencia en este tema está disponible para los usuarios con acceso a todo BMJ Best Practice.

Diferenciales
- Whiplash injury (cervical myofascial strain)
- Acute disk herniation
- Metastatic malignancy
Más DiferencialesGuías de práctica clínica
- ACR appropriateness criteria: cervical pain or cervical radiculopathy
- A clinical practice guideline for the management of patients with degenerative cervical myelopathy: recommendations for patients with mild, moderate, and severe disease and nonmyelopathic patients with evidence of cord compression
Más Guías de práctica clínicaFolletos para el paciente
Back pain (lower back)
Más Folletos para el pacienteInicie sesión o suscríbase para acceder a todo el BMJ Best Practice
El uso de este contenido está sujeto a nuestra cláusula de exención de responsabilidad