Investigations
1st investigations to order
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) cell count and differential
Test
A lumbar puncture to obtain CSF is the most important investigation when a diagnosis of bacterial meningitis is suspected; however, if lumbar puncture is delayed (e.g., due to awaiting imaging), this should not delay initiation of antibiotics.[59]
In untreated bacterial meningitis, typical findings in the CSF include pleocytosis, with WBC count typically >1000 cells/microliter and predominance of polymorphonuclear leukocytes.
More than 90% of patients present with CSF WBC count >100/microliter.[42] However, CSF WBC count can be normal in the early phase of the disease and in neonates.[65]
How to perform a diagnostic lumbar puncture in adults. Includes a discussion of patient positioning, choice of needle, and measurement of opening and closing pressure.
Result
polymorphonuclear pleocytosis
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) protein
Test
In bacterial meningitis, CSF protein is usually elevated (>1.5 g/L; normal <0.5 g/L).[94]
Result
elevated
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) glucose
Test
In bacterial meningitis, CSF glucose concentration is <45 mg/dL (<2.5 mmol/L), or <40% of simultaneously measured serum glucose.[42]
Result
low
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Gram stain
Test
Gram staining typically reveals the organism in 80% of cases.[42][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: species bacteriaImage provided by the CDC Public Health Image Library [Citation ends].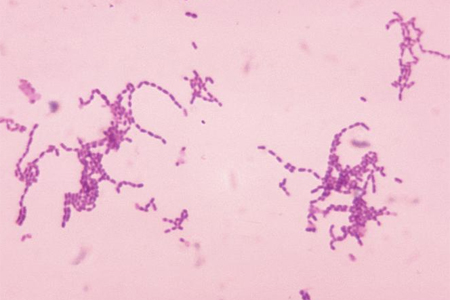
However, diagnostic yields may be lower in patients who have received antibiotics before cultures are obtained.
Result
positive
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) culture
Test
Bacterial culture of CSF is positive in 80% of untreated cases.[42]
However, diagnostic yields may be lower in patients who have received antibiotics before cultures are obtained.
Result
positive
antigen detection in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Test
Serogroup A, B, C, Y, and W-135 polysaccharide antigen can be detected by latex agglutination in 22% to 93% of patients with meningococcal meningitis.[4] Antigen may persist in CSF for several days, making this test useful in patients treated with antibiotics before diagnostic specimens have been obtained and for the rapid presumptive diagnosis of meningococcal infection. Serogroup B Neisseria meningitidis and serotype K1 Escherichia coli polysaccharides cross-react, so test results should be interpreted cautiously in neonates. Antigen detection testing on body fluids other than CSF, including serum or urine, is not recommended because of poor sensitivity and specificity.
Result
N meningitidis capsular polysaccharide antigen
blood culture
Test
Performed ideally before giving antibiotics. However, taking blood for culture should not delay administration of antibiotics. The results of blood cultures may be influenced by previous antimicrobial therapy. For example, in one retrospective review, blood cultures were positive in approximately 50% of untreated patients with meningococcal disease, compared with only 5% of patients who received an antibiotic before admission.[79]
Result
positive
CBC and differential
Test
Patients with bacterial meningitis may have an elevated WBC with a polymorphonuclear predominance. Patients with rapidly progressive infections, however, may initially have normal WBC. Neutropenia is not uncommon in severe infections. Thrombocytopenia and mild anemia are common.
Result
leukocytosis, anemia, thrombocytopenia
CRP
Test
Serum CRP tends to be elevated in patients with bacterial meningitis.
In patients where the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Gram stain is negative and the differential diagnosis is between bacterial and viral meningitis, a normal serum CRP concentration excludes bacterial meningitis with approximately 99% certainty.[80][81]
Result
high
electrolytes, calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), glucose
Test
Patients with severe bacterial meningitis often have metabolic abnormalities, especially acidosis, hypokalemia, hypoglycemia, and hypocalcemia.
Result
acidosis, low Ca/Mg, or hyper/hypoglycemia
coagulation profile (prothrombin time, INR, activated PTT, fibrinogen, fibrin degradation products)
Test
Coagulopathy is common in severe meningitis infections. Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is caused by acquired deficiencies of protein C, protein S, and antithrombin III; increases in plasminogen activator inhibitor and thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor; and reduced activation of protein C on endothelial cells.
Result
evidence of DIC (prolonged thrombin time, elevated fibrin degradation products or D-dimer, low fibrinogen or antithrombin levels)
CT head
Test
Cranial CT scan should be considered before lumbar puncture in the presence of focal neurologic deficit, new-onset seizures, papilledema, altered mental state, or immunocompromised state to exclude a brain abscess or generalized cerebral edema.[59]
Cranial imaging may be used to identify underlying conditions and meningitis-associated complications.
Brain infarction, cerebral edema, and hydrocephalus are common findings especially in pneumococcal meningitis.[86]
Result
normal or raised intracranial pressure or intracranial lesion if other pathologies present
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Test
PCR amplification of bacterial DNA from blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is more sensitive and specific than traditional microbiologic techniques. It is useful in distinguishing bacterial from viral meningitis.
PCR may also be helpful in diagnosing bacterial meningitis in patients who have been pretreated with antibiotics.[73]
Real-time PCR assay can identify specific serogroup ( Neisseria meningitidis) or serotype ( Haemophilus influenzae) from clinical isolates (typically blood or CSF).[95]
Multiplex PCR (such as the QIAstat-Dx Meningitis/Encephalitis [ME] Panel or the BioFire FilmArray ME Panel) is used to rapidly screen for multiple causative pathogens in a single reaction.[76][77][78]
Result
positive
Investigations to consider
MRI head
Test
Should be used if there are focal neurologic signs.
Cranial imaging may be used to identify underlying conditions and meningitis-associated complications.
Brain infarction, cerebral edema, and hydrocephalus are common findings especially in pneumococcal meningitis.[86]
Result
normal or intracranial lesion if other pathologies present
transcranial Doppler
Test
Can be considered if there are concerns for vasculopathy associated with bacterial meningitis.[87]
Result
intracranial arterial stenosis of the middle cerebral artery and ischemia most common findings in acute meningitis
serum procalcitonin
Test
Sensitivity and specificity greater than 90% when used to distinguish between bacterial and viral meningitis.[82][83][84] Do not perform procalcitonin testing without an established, evidence-based protocol. When used appropriately, there are significant opportunities to decrease unnecessary antimicrobial use.[85]
Result
normal or elevated
Emerging tests
heparin-binding protein (HBP)
Test
May have a role as a possible rapid biomarker for bacterial infections. In systematic review and meta-analysis studies, HBP showed a high diagnostic accuracy of bacterial infections, including urinary tract infection and meningitis. However, further studies are needed to determine its prognostic value and whether it could guide antibiotic therapy.[88]
Result
elevated in bacterial infections
rapid antigen cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) tests
Test
May be useful in triaging pneumococcal meningitis.
A large systematic review and meta-analysis looked at using rapid antigen tests in CSF to triage and diagnose pneumococcal meningitis. The studies found the rapid antigen tests to have a sensitivity and specificity of 99.5% (95% CI 92.4% to 100%) and 98.2% (95% CI 96.9% to 98.9%), respectively. Further studies are warranted to investigate the accuracy of ruling out pneumococcal meningitis based on the results of these tests.[89]
Result
positive
metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS)
Test
Diagnostic technique that sequences all the DNA and RNA in a sample to identify microbes. A systematic review and meta-analysis showed that in cases of unexplained bacterial meningoencephalitis, the mNGS of cerebrospinal fluid samples offered an advantage over conventional methods, especially in complex cases when a rare pathogen is implicated or the patient is on antibiotics.[90]
Result
positive
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer

