Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- family history of Marfan disease
- tall stature
- wide arm span
- high level of pubic bone
- high arched palate
- arachnodactyly
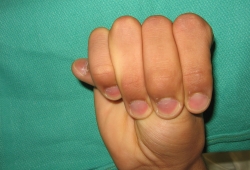
- positive wrist sign
- positive thumb sign
- pectus excavatum (funnel chest)
- pectus carinatum (pigeon breast)
- scoliosis
- flat feet (pes planus)
- dislocated/subluxed eye lens
- myopia and/or astigmatism
- retinal abnormalities
- joint hypermobility
- aortic valve murmur
- mitral valve murmur
- history of treatment for dental crowding
- history of myopia and/or astigmatism
- reduced elbow extension
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- glaucoma
- history of spontaneous pneumothorax
- striae
- low back ache
- joint pain
- inguinal/abdominal/incisional hernias
- dyspnea
- signs of heart failure
Fatores de risco
- family history of Marfan syndrome
- family history of aortic dissection or aneurysm
- high paternal age
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- echocardiography
- slit-lamp eye exam with intraocular pressure measurement
- CT scan, thorax
- MRI, thorax
Investigações a serem consideradas
- blood screening for fibrillin-1 (FBN-1) gene mutation
- CXR
- CT scan, abdomen
- MRI, abdomen
- ultrasound, abdomen
- CT scan, lower spine
- MRI, lower spine
- plasma homocysteine
Algoritmo de tratamento
aortic dilation meeting the indications for surgery
retinal tear
retinal detachment
aortic dilation not meeting indications for surgery or following aortic surgery
myopia
lens subluxation/dislocation
cataract
scoliosis/kyphoscoliosis
severe pectus excavatum/carinatum with evidence of cardiopulmonary compromise
arthropathy and/or spondylolisthesis
Colaboradores
Autores
Anne Child, MD, FRCP
Medical Director Marfan Trust
Honorary Consultant Royal Brompton Group GSTT NHS Foundation Trust
Keston
Kent
UK
Declarações
AC is an author of several references cited in this topic but has no competing interests.
Agradecimentos
Dr Anne Child would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Aman Chandra and Dr Maite Tome, the previous contributors to this topic. Dr Anne Child and Dr Aman Chandra would also like to thank Anna Apara for her work on this topic.
Declarações
AC, MT, and AA declare that they have no competing interests.
Revisores
Daniel Judge, MD
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Medical Director
JHU Center for Inherited Heart Disease
Johns Hopkins Hospital
Baltimore
MD
Declarações
DJ declares that he has no competing interests.
Reed E. Pyeritz, MD, PhD
Professor of Medicine and Genetics
University of Pennsylvania
Philadelphia
PA
Declarações
REP declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Tinkle BT, Lacro RV, Burke LW, et al. Health supervision for children and adolescents with Marfan syndrome. Pediatrics. 2023 Apr 1;151(4):e2023061450. Resumo
Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Black JH 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-482.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Aortic dissection not associated with Marfan syndrome
- Bicuspid aortic valve
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease
- 2014 ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases
Mais DiretrizesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal