Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- chest pain
- dyspnea
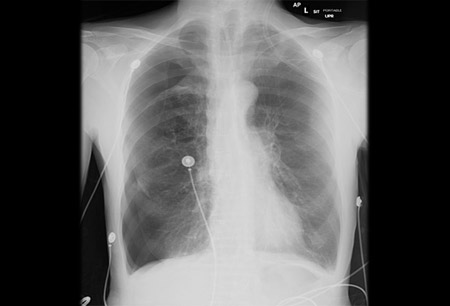
- hyperexpanded ipsilateral hemithorax
- hyper-resonant ipsilateral hemithorax
- ipsilateral absent or diminished breath sounds
- extreme breathlessness
- trachea shifted to contralateral side
Risk factors
- cigarette smoking
- family history of pneumothorax
- tall and slender body build
- age <40 years
- recent invasive medical procedure
- chest trauma
- acute severe asthma
- COPD
- tuberculosis
- AIDS-related Pneumocystis jirovecii infection
- cystic fibrosis
- lymphangioleiomyomatosis
- Marfan syndrome
- homocystinuria
- primary lung cancer and metastatic cancer to the lungs
- Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome
- pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis
- Erdheim-Chester disease
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- chest x-ray
- chest ultrasound
Tests to consider
- CT chest
- bronchoscopy
Treatment algorithm
tension pneumothorax
primary spontaneous pneumothorax AND patient ≤ 50 years old
secondary spontaneous pneumothorax OR patient > 50 years old
traumatic pneumothorax
pneumothorax ex vacuo
catamenial pneumothorax
Contributors
Authors
Christopher Kapp, MD
Assistant Professor of Medicine, Interventional Pulmonologist
Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care, Section of Interventional Pulmonary
Northwestern Memorial Hospital
Chicago
IL
Disclosures
CK declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Christopher Kapp would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Lonny Yarmus, Dr Jason Akulian, Dr Ryland P. Byrd Jr, Dr Thomas M. Roy, and Dr Anita Alwani, previous contributors to this topic.
Declarações
LY, JA, RPB, TMR, and AA declare that they have no competing interests.
Revisores
Marc Noppen, MD
Professor and Chief Executive Officer of Respiratory Division
Interventional Endoscopy Clinic
University Hospital Brussels
Brussels
Belgium
Declarações
MN declares that he has no competing interests.
Steve A. Sahn, MD
Professor of Medicine
Division of Pulmonary Critical Care, Allergy and Sleep Medicine
Medical University of South Carolina
Charleston
SC
Declarações
SAS declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
British Thoracic Society. Guidelines: pleural disease. Jul 2023 [internet publication].Texto completo
American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: intensive care unit patients. 2020 [internet publication].Texto completo
American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: rib fractures. 2018 [internet publication].Texto completo
British Thoracic Society. Clinical statements: pleural procedures. Jul 2023 [internet publication].Texto completo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Asthma, acute exacerbation
- COPD, acute exacerbation
- Pulmonary embolism
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- BTS Guidelines on Pleural Disease
- ACR appropriateness criteria: intensive care unit patients
Mais DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Pneumothorax
Chest drain insertion
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesVideos
Needle decompression of tension pneumothorax: animated demonstration
Insertion of intercostal drain, Seldinger technique: animated demonstration
Mais vídeosConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal