Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- chronic erosive blistering of the skin, mucosa, or both
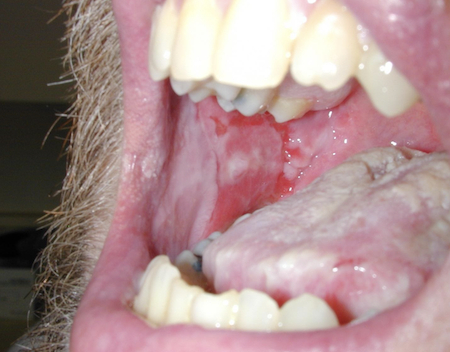
- chronic mouth erosions (PV, PNP)
- painful lips (PNP)
- shortness of breath (PNP)
Other diagnostic factors
- pruritic scalp (PV, PF)
- bloody nose (PV, PNP)
- painful skin (PV, PF, PNP)
- dysphagia (PV)
- pruritic skin (PV, PF)
- conjunctivitis (PV, PNP)
Risk factors
- increasing age
- HLA DR4 (PV)
- HLA DQ1 (PV)
- HLA DRB1 (PNP)
- associated malignancy (PNP)
- penicillamine use
- ACE inhibitors use
- penicillin use
- tiopronin use
- interleukin-2 use
- nifedipine use
- rifampin use
- exposure to hematophagous insects
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- skin biopsy, hematoxylin and eosin stain
- skin biopsy, direct immunofluorescence
Tests to consider
- indirect immunofluorescence on serum
- serum ELISA
- upper gastrointestinal endoscopy
- CXR
- chest CT scan
- PFT
- serum immunoblot (Western blot)
Treatment algorithm
mild pemphigus vulgaris
mild pemphigus foliaceus
moderate to severe pemphigus vulgaris or pemphigus foliaceus
paraneoplastic pemphigus
moderate to severe pemphigus vulgaris or pemphigus foliaceus 6 months after initial therapy: with disease control/complete remission
moderate to severe pemphigus vulgaris or pemphigus foliaceus 6 months after initial therapy: without complete remission
moderate to severe pemphigus vulgaris or pemphigus foliaceus 12 to 18 months after initial therapy: complete remission
severe/refractory pemphigus
Contributors
Authors
Jon H. Meyerle, MD
Associate Professor
Department of Dermatology
Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences
Bethesda
MD
Disclosures
JHM declares that he has no competing interests.
Grant J. Anhalt, MD
Professor
Department of Dermatology
Johns Hopkins Medical Institution
Baltimore
MD
Disclosures
GJA declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Daniel Mimouni, MD
Professor
Department of Dermatology
Rabin Medical Center
Petah Tikva
Israel
Disclosures
DM declares that he has no competing interests.
Vesna Petronic-Rosic, MD, MSc
Associate Professor and Clinical Director
Section of Dermatology
University of Chicago
Chicago
IL
Disclosures
VPR declares that she has no competing interests.
Timothy Patton, MD
Assistant Professor of Dermatology
Department of Dermatology
University of Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh
PA
Disclosures
TP declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Joly P, Horvath B, Patsatsi Α, et al. Updated S2K guidelines on the management of pemphigus vulgaris and foliaceus initiated by the european academy of dermatology and venereology (EADV). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 Sep;34(9):1900-13.Full text Abstract
Antiga E, Bech R, Maglie R, et al. S2k guidelines on the management of paraneoplastic pemphigus/paraneoplastic autoimmune multiorgan syndrome initiated by the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023 Jun;37(6):1118-34.Full text Abstract
Murrell DF, Peña S, Joly P, et al. Diagnosis and management of pemphigus: recommendations of an international panel of experts. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Mar;82(3):575-85.e1.Full text Abstract
Joly P, Maho-Vaillant M, Prost-Squarcioni C, et al. First-line rituximab combined with short-term prednisone versus prednisone alone for the treatment of pemphigus (Ritux 3): a prospective, multicentre, parallel-group, open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2017 May 20;389(10083):2031-40. Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Familial benign pemphigus (Hailey-Hailey disease)
- Bullous pemphigoid (BP)
- Linear IgA bullous dermatosis
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Updated S2K guidelines on the management of paraneoplastic pemphigus/paraneoplastic autoimmune multiorgan syndrome initiated by the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV)
- S2k guidelines on the management of paraneoplastic pemphigus/paraneoplastic autoimmune multiorgan syndrome initiated by the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV)
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer