Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- elevated serum aminotransferases
- history of hepatitis
- acute liver failure
- behavioral abnormalities
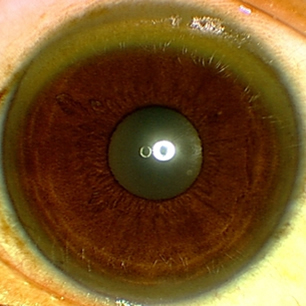
- presence of Kayser-Fleischer rings
- tremor
- dysarthria
- dystonia
- incoordination
- sloppy or small handwriting
Other diagnostic factors
- cognitive impairment
- depression
- personality change
- dysdiadochokinesis
- abnormal extraocular movements
- normal sensation, muscular strength, and reflexes
- history of gastrointestinal bleeding
- jaundice
- liver tenderness
- spider angiomata
- gynecomastia
- ascites
- peripheral edema
- bruising
- encephalopathy
- dysphagia
Risk factors
- ATP7B gene mutation
- family history of Wilson disease
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- LFTs
- 24-hour urinary copper
- slit-lamp exam
- serum ceruloplasmin
Investigations to consider
- CBC
- liver biopsy
- MRI brain
- non-ceruloplasmin-bound copper concentration (NCC)
- DNA testing for ATP7B mutations
Emerging tests
- direct measurement of ATP7B peptide
Treatment algorithm
hepatic failure, severe (Nazer score ≥10 or New Wilson Index score ≥11)
hepatic failure, mild to moderate (Nazer score ≤9 or New Wilson Index score ≤10)
symptomatic (neurologic disease or hepatic disease without liver failure)
asymptomatic
Contributors
Authors
Michael L. Schilsky, MD, FAASLD
Professor of Medicine and Surgery
Divisions of Digestive Diseases and Transplant and Immunology
Yale School of Medicine
New Haven
CT
Disclosures
MS is an author of multiple references in this topic.
Uyen Kim To, MD
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Division of Digestive Diseases
Yale School of Medicine
New Haven
CT
Disclosures
UKT declares that she has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Professor Michael Schilsky and Dr Uyen Kim To would like to gratefully acknowledge Professor George Brewer, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
GB is an author of several references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Jeff Bronstein, MD, PhD
Director of Movement Disorders
David Geffen School of Medicine
University of California, Los Angeles
Los Angeles
CA
Disclosures
JB has received grants from and consulted for Alexion and Ultragenix. JB is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Giacomo C. Sturniolo, MD
Professor of Gastroenterology
Department of Surgical and Gastroenterological Sciences
University of Padua
Padova
Italy
Disclosures
GCS declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.Full text Abstract
Shribman S, Marjot T, Sharif A, et al; British Association for the Study of the Liver Rare Diseases Special Interest Group. Investigation and management of Wilson's disease: a practical guide from the British Association for the Study of the Liver. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jun;7(6):560-75. Abstract
Socha P, Janczyk W, Dhawan A, et al. Wilson's disease in children: a position paper by the Hepatology Committee of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018 Feb;66(2):334-44.Full text Abstract
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: Wilson's disease. J Hepatol. 2012 Mar;56(3):671-85.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
- Hemochromatosis
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- ACR Appropriateness Criteria®: abnormal liver function tests
- Multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease
More GuidelinesPatient information
Hepatitis C: what is it?
Hepatitis C: what are the treatment options?
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer