Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- hoarseness
- dysphagia
- sore throat
- odynophagia
- cough
- hyperemia of the oropharynx
- history of heavy vocal use
- gastroesophageal reflux
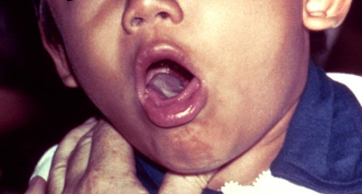
- oropharyngeal white-gray exudates
Other diagnostic factors
- rhinitis
- fatigue and malaise
- fever
- enlarged tonsils
- enlarged, tender anterior cervical lymph nodes
- postnasal drip
- dyspnea
- weight loss
- tonsillopharyngeal exudate
- acute respiratory distress
- toxic appearance
- drooling
- stridor
Risk factors
- recent history of upper respiratory infection
- incomplete or absent Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib) vaccination
- incomplete or absent diphtheria vaccination
- contact with infected individual
- travel to area where diphtheria or tuberculosis are endemic
- HIV or other immunocompromise
- use of inhaled corticosteroids or prolonged courses of antibiotics
- heavy vocal use
- tobacco use
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- laryngoscopy
Tests to avoid
- computed tomography (CT)
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- viral panel testing
Tests to consider
- biopsy
- oropharyngeal cultures
- nasal swab for culture
- serum immunoprecipitation or polymerase chain reaction for diphtheria
- complete blood count
- rapid antigen detection test
- chest x-ray
- sputum cultures
- videostroboscopy
Treatment algorithm
with potential airway compromise
viral
suspected bacterial: nondiphtheria and nontuberculous
confirmed diphtheria
tuberculosis
fungal
vocal strain
Contributors
Authors
Vaninder Kaur Dhillon, MD
Assistant Professor
Johns Hopkins University
Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery
Divisions of Laryngology and Endocrine Head and Neck Surgery
Bethesda
MD
Disclosures
VKD declares that she has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Vaninder Kaur Dhillon would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Chad W. Whited, Dr Seth H. Dailey and Dr Ozlem E. Tulunay-Ugur, the previous contributors to this topic. CWW, SHD and OETU declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Michael Johns, MD
Director
Assistant Professor
Emory University
Atlanta
GA
Disclosures
MJ declares that he has no competing interests.
James Suen, MD
Chair; Professor
University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
Department of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery
Little Rock
AR
Disclosures
JS declares that he has no competing interests.
Remco de Bree, MD, PhD
Otolaryngologist
Head and Neck Surgeon
VU University Medical Center
Amsterdam
The Netherlands
Disclosures
RdB declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
House S A, Fisher E L. Hoarseness in adults. Am Fam Physician. 2017 Dec 1;96(11):720-8.Full text
Dworkin JP. Laryngitis: types, causes, and treatments. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2008 Apr;41(2):419-36. Abstract
Stachler RJ, Francis DO, Schwartz SR, et al. Clinical practice guideline: hoarseness (dysphonia) (update). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Mar;158(1_suppl):S1-S42.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Tonsillitis
- Infectious mononucleosis
- Allergic rhinitis
More Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Clinical practice guideline: hoarseness (dysphonia)
- Sore throat (acute): antimicrobial prescribing
More DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Sore throat
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal