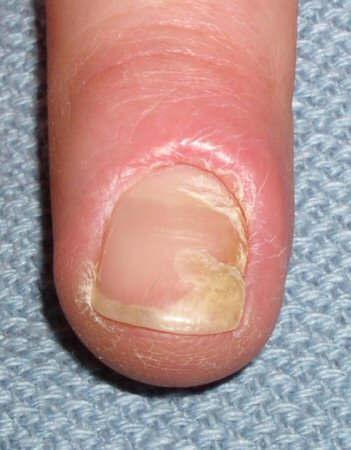
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presence of risk factors
- pain, swelling, drainage (acute)
- swollen, purulent nail fold (acute)
- nail plate irregularities (chronic)
- swelling/redness of nail folds (chronic)
- pink, swollen nail folds (chronic)
- missing cuticle (chronic)
- underlying nail plate abnormalities (chronic)
Risk factors
- microscopic or macroscopic injury to the nail folds (acute)
- occupational risks (acute and chronic)
- barrier damage to the nail folds, cuticle (chronic)
- ingrown nail
- medications (chronic)
- toddler and adult
- female
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- swab for Gram stain, culture, and sensitivity (acute or acute-on-chronic)
- swab for Tzanck smear (acute, herpetic)
Tests to consider
- potassium hydroxide or fungal culture (chronic)
- x-ray
- MRI
- biopsy of skin/bone
Treatment algorithm
acute paronychia
chronic paronychia
retronychia
Contributors
Authors
Shirin Zaheri, MBBS, BSc, MRCP
Dermatology Consultant
Charing Cross Hospital
Imperial College NHS Trust
London
UK
Disclosures
SZ declares that she has no competing interests.
Khawar Hussain, BSc, MRCP, FHEA
Specialty Registrar in Dermatology
Charing Cross Hospital
Imperial College NHS Trust
London
UK
Disclosures
KH has been reimbursed by Sanofi for conference travel expenses.
Acknowledgements
Dr Shirin Zaheri and Dr Khawar Hussain would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Catherine Hardman, Dr Nathaniel J. Jellinek, Professor C. Ralph Daniel III, and Dr Shaimaa Nassar, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
NJJ, CH, and SN declare that they have no competing interests. CRD is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Shehla Admani, MD
Clinical Assistant Professor of Dermatology
Stanford University School of Medicine
San Jose
CA
Disclosures
SA declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Daniel CR 3rd. Paronychia. Dermatol Clin. 1985 Jul;3(3):461-4. Abstract
Leggit JC. Acute and chronic paronychia. Am Fam Physician. 2017 Jul 1;96(1):44-51.Full text Abstract
Relhan V, Goel K, Bansal S, et al. Management of chronic paronychia. Indian J Dermatol. 2014 Jan;59(1):15-20.Full text Abstract
Shafritz AB, Coppage JM. Acute and chronic paronychia of the hand. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014 Mar;22(3):165-74. Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
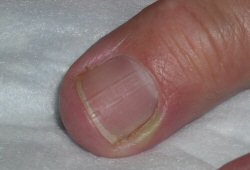
Differentials
- Herpetic whitlow
- Arthropod bite or sting
- Traumatic injury
More DifferentialsPatient information
Dermatitis
Fungal nail infections
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer