Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- severe diffuse or localized pain in an extremity
- fever
- localized swelling or erythema
- hypotension
- diffuse, scarlatina-like erythematous rash
Other diagnostic factors
- acute mental status changes
- influenza-like symptoms
- muscular tenderness and weakness
- gastrointestinal symptoms
- features of myocarditis
- endophthalmitis
- hypothermia
Risk factors
- diabetes mellitus
- alcohol-use disorder
- minor trauma and injuries with bruising, hematoma formation, or muscle strain
- surgical procedures (e.g., vaginal delivery, breast reconstruction, cesarean section, hysterectomy, liposuction, bunionectomy)
- prolonged use (>6 hours) of single tampon
- use of highly absorbent tampons
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) use
- use of contraceptive sponges, diaphragms, and IUDs
- untreated strep throat
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- microscopy and culture (blood, wound, fluid, tissue)
- CBC
- coagulation profile
- serum BUN and creatinine
- urinalysis
- LFTs
- creatine kinase (CK)
- serum calcium
- serum sodium
- serum phosphorus
- serum albumin
- serum lactic acid
Tests to consider
- Staphylococcus aureus antibody testing
- chest x-ray
Emerging tests
- serotyping
Treatment algorithm
suspected toxic shock syndrome
confirmed streptococcal toxic shock syndrome
confirmed staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome: methicillin-sensitive
confirmed staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome: methicillin-resistant
clinical toxic shock syndrome without confirmed cultures
Contributors
Authors
Brit Jeffrey Long, MD
Attending Physician
Associate Professor of Emergency Medicine
Department of Emergency Medicine
Brooke Army Medical Center
Fort Sam Houston
TX
Disclosures
BJL declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Brit J. Long would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Marie R. Baldisseri and Dr Walid Khayr, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
MRB and WK declare they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Mary Jane Reed, MD, FACS, FASMBS
Associate Professor
Department of Critical Care Medicine and Department of General Surgery
Geisinger Medical Center
Danville
PA
Disclosures
MJR declares that she has no competing interests.
Janice Zimmerman, MD
Head
Critical Care Division
The Methodist Hospital
Houston
TX
Disclosures
JZ declares that she has no competing interests.
Djillali Annane, MD, PhD
Professor in Medicine at University of Versailles SQY
Director of the General ICU at Raymond Poincaré Hospital (AP-HP)
Director of the Center for Clinical Research and Technology Innovation (INSERM)
Garches
France
Disclosures
DA is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome (STSS): 2010 case definition. 2010 [internet publication].Full text
Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Crit Care Med. 2021 Nov 1;49(11):e1063-143.Full text Abstract
Stevens DL, Bisno AL, Chambers HF, et al. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of skin and soft tissue infections: 2014 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;59:e10-e52.Full text Abstract
Sartelli M, Guirao X, Hardcastle TC, et al. 2018 WSES/SIS-E consensus conference: recommendations for the management of skin and soft-tissue infections. World J Emerg Surg. 2018;13:58.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
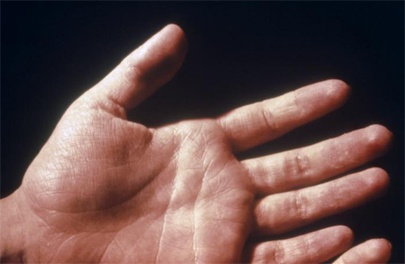
Differentials
- Gram-negative sepsis
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF)
- Acute meningococcemia
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2021
- Invasive group A streptococcal disease: management and chemoprophylaxis
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer