Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- upper and lower respiratory tract involvement
- renal involvement
- constitutional features
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- ocular manifestations
- cutaneous manifestations
- musculoskeletal manifestations
- neurologic manifestations
- signs or symptoms of thromboembolism
- gastrointestinal involvement
- cardiac involvement
- breast mass
- lower genitourinary tract involvement
- endocrine involvement
- isolated mass lesions/focal granuloma
Fatores de risco
- genetic predisposition
- infection
- environmental exposures
- white ethnicity
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- urinalysis and microscopy
- CT chest
- antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)
- CBC and differential
- serum creatinine
- C-reactive protein
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- liver function tests
- serum calcium
Investigações a serem consideradas
- tissue biopsy
- pulmonary function testing
- bronchoscopy
- electromyography/nerve conduction studies
- upper airway endoscopy
- CT sinuses
Algoritmo de tratamento
severe (life/organ-threatening) disease: remission induction
nonsevere (non-life/organ-threatening) disease: remission induction
remission successfully induced
relapse following successful remission
Colaboradores
Autores
Eamonn Molloy, MD, MS, FRCPI
Consultant Rheumatologist
Department of Rheumatology
St Vincent's University Hospital
Dublin
Ireland
Declarações
EM declares that he has been a speaker for, and participated in advisory board for Abbvie, Janssen, Gilead, Novartis. He has received sponsorship to attend conferences from Abbvie, Janssen and UCB, and received research funding from Abbvie.
Revisores
Curry L. Koening, MD, MS
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Rheumatology Division
University of Utah School of Medicine
Salt Lake City
UT
Declarações
CLK declares that he has no competing interests.
Jaap M. van Laar, MD, PhD
Professor of Clinical Rheumatology
Musculoskeletal Research Group
Institute of Cellular Medicine
Newcastle University
The Medical School
Newcastle upon Tyne
UK
Declarações
JMVL declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Chung SA, Langford CA, Maz M, et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology/Vasculitis Foundation guideline for the management of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2021 Aug;73(8):1088-105.Texto completo Resumo
Hellmich B, Sanchez-Alamo B, Schirmer JH, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of ANCA-associated vasculitis: 2022 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023 Mar 16:ard-2022-223764.Texto completo Resumo
Stone JH, Merkel PA, Spiera R, et al; RAVE-ITN Research Group. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide for ANCA-associated vasculitis. N Engl J Med. 2010 Jul 15;363(3):221-32.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
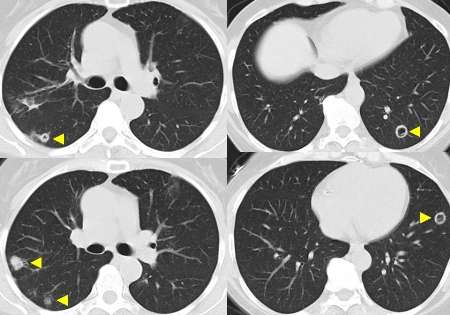
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA, Churg-Strauss syndrome)
- Microscopic polyangiitis (MPA)
- Classic polyarteritis nodosa (cPAN)
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- KDIGO 2024 clinical practice guideline for the management of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) associated vasculitis
- Guideline for vaccinations in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal disease
Mais DiretrizesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal