Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- inability to bear weight
- pain in affected leg/hip
- pain with hip movement
Other diagnostic factors
- shortened and externally rotated leg
Risk factors
- osteoporosis/osteopenia
- age over 65 years
- falls
- low body mass index
- female sex
- high-energy trauma
- medications
- ethnicity
- dementia
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- plain x-rays
Investigations to consider
- MRI pelvis (without contrast)
- CT pelvis (without contrast)
Treatment algorithm
intracapsular (femoral neck) fracture
extracapsular (intertrochanteric) fracture
Contributors
Expert advisers
Herman Johal, MD, MPH, FRCSC
Orthopaedic Trauma Surgeon
Assistant Professor
Department of Surgery
McMaster University
Hamilton, Ontario
Canada
Disclosures
HJ declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Herman Johal would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Bradley A. Petrisor and Dr Mohit Bhandari, the previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
BAP and MB declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Marc F. Swiontkowski, MD
Professor
Department of Orthopedic Surgery
University of Minnesota
Minneapolis
MN
Disclosures
MFS is Editor-in-Chief of the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery.
Rudolf Poolman, MD, PhD
Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis
Teaching Hospital with The University of Amsterdam
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
Amsterdam
The Netherlands
Disclosures
RP has been reimbursed by LINK for organizing education and research consultancy.
David Hackam, MD, PhD
Assistant Professor of Surgery
Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh
PA
Disclosures
DH declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Management of hip fractures in older adults: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. December 2021 [internet publication].Full text
American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: acute hip pain. 2024 [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
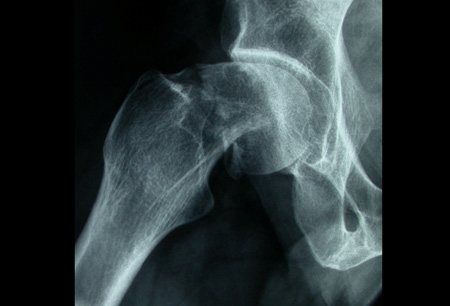
Differentials
- Acetabular fracture
- Pubic rami fracture
- Femoral shaft or subtrochanteric femur fracture
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- ACR appropriateness criteria: acute hip pain
- Perioperative management of antithrombotic therapy
More GuidelinesPatient information
Osteoporosis
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer