Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- fever ≥102.2°F (≥39.0°C)
- arthralgia
- arthritis
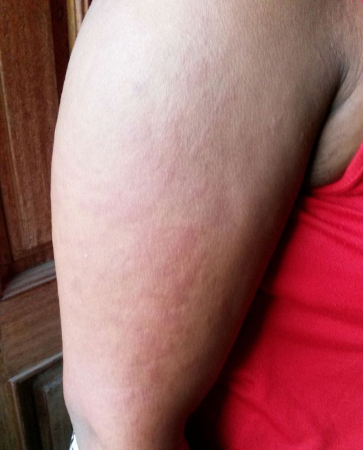
- salmon-colored maculopapular skin rash
Other diagnostic factors
- dermatographic urticaria
- sore throat
- myalgia
- lymphadenopathy
- pleuritis
- splenomegaly
- hepatomegaly
- pericarditis
- myocarditis
- signs of macrophage activation syndrome (MAS)
Risk factors
- female sex
- young adult age
- preceding infection (e.g., with cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, rubella, Mycoplasma)
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- CBC
- renal panel
- C-reactive protein (CRP)
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- liver function tests
- procalcitonin
- blood cultures
- chest x-ray
- renal and liver ultrasound scan
- echocardiogram
- ECG
Investigations to consider
- cardiac enzymes
- cardiac MRI
- serum ferritin
- glycosylated ferritin
- further tests as part of full septic screen
- further tests as part of autoimmune/rheumatologic screen
- fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)-positron emission tomography (PET) whole-body scan
- whole-body CT scan
- bone marrow biopsy
- lymph node biopsy
- empirical corticosteroid trial
- autoinflammatory gene profiling
Emerging tests
- cytokine profiles
- serum S100A12; serum calprotectin (S100A8/S100A9 dimer)
- HLA genotyping
Treatment algorithm
severe disease: with severe organ dysfunction with or without signs of macrophage activation syndrome
mild or moderate disease: no severe organ dysfunction or signs of macrophage activation syndrome
Contributors
Authors
Sinisa Savic, MRCP, FRCPath, PhD
Associate Professor (Clinical)
Leeds Institute of Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Medicine
Consultant
Department of Clinical Immunology and Allergy
St James’s University Hospital
Clinical Lead for Allergy and Immunology
The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust
Leeds
UK
Disclosures
SS has received payment for consulting services from Novartis, Takeda, SOBI, BioCryst, CSL Behring, and Kalvista. Speaking/educational events Takeda, Novartis, SOBI, and SCL Behring. Research grants SOBI and CSL Behring.
Adam Al-Hakim, BMBS, MRCP, BMedSci
Specialty Registrar in Clinical Immunology and Allergy
St James’s University Hospital
The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust
Leeds
UK
Disclosures
AA declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Sreelakshmi Panginikkod, MD, FACP, FACR
Assistant Professor in Rheumatology and Associate Program Director for Rheumatology
Tufts University School of Medicine
Boston
MA
Disclosures
SP declares that she has no competing interests.
James Galloway, MBChB, MSc, PhD, FRCP
Professor of Rheumatology
King’s College London
Honorary Consultant Rheumatologist
King’s College Hospital
London
UK
Disclosures
JG declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Giacomelli R, Ruscitti P, Shoenfeld Y. A comprehensive review on adult onset Still's disease. J Autoimmun. 2018 Sep;93:24-36.Full text Abstract
Vordenbäumen S, Feist E, Rech J, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of adult-onset Still's disease: a concise summary of the German society of rheumatology S2 guideline. Z Rheumatol. 2023 Feb;82(suppl 2):81-92.Full text Abstract
Macovei LA, Burlui A, Bratoiu I, et al. Adult-onset Still's disease-a complex disease, a challenging treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 24;23(21):12810.Full text Abstract
Efthimiou P, Kontzias A, Hur P, et al. Adult-onset Still's disease in focus: clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment, and unmet needs in the era of targeted therapies. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2021 Aug;51(4):858-74.Full text Abstract
Yamaguchi M, Ohta A, Tsunematsu T, et al. Preliminary criteria for classification of adult Still's disease. J Rheumatol. 1992 Mar;19(3):424-30. Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Sepsis
- Infectious endocarditis
- Biliary infection
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Diagnosis and treatment of adult-onset Still's disease: a concise summary of the German society of rheumatology S2 guideline
- Evidence-based clinical practice guideline for adult Still’s disease
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer