Resumo
Definition
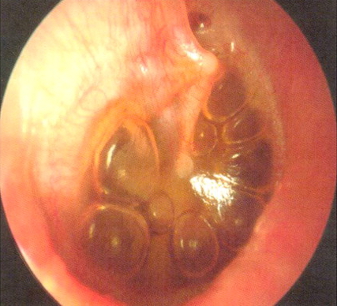
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- middle ear effusion
- no signs of acute infection
- aural fullness or pressure
- hearing loss
Other diagnostic factors
- slow progress within an education setting
- failed hearing screen
- speech delay
- signs of ear discomfort
- behavior problems
- impaired gross motor skills and balance problems
Risk factors
- childhood
- upper respiratory tract infection
- acute otitis media
- craniofacial anomalies
- Eustachian tube dysfunction
- genetic predisposition in children
- daycare attendance
- adenoid hyperplasia, adenoiditis
- allergic rhinitis
- environmental tobacco smoke
- sinonasal disease
- nasopharyngeal malignancy
- gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- low socioeconomic status
- male sex
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- pneumatic otoscopy
- tympanometry
- audiology
Investigations to consider
- nasopharyngeal endoscopy
Treatment algorithm
duration <3 months
duration ≥3 months
Contributors
Authors
Jennifer Shin, MD, SM
Associate Professor of Otology and Laryngology
Vice Chair for Academic Affairs at Longwood
Department of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery
Harvard Medical School
Boston
MA
Disclosures
JJS receives book royalties from Evidence-Based Otolaryngology, Shin JJ, Randolph GW, editors; New York: Springer, 2008 and Otolaryngology Prep and Practice, Shin JJ, Cunningham MJ, editors; Plural Publishing, 2013. JJS is a recipient of funding from American Academy of the Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Foundation, the Brigham Care Redesign Program Award, the BWell Funds Awards and a Brigham Innovations Award.
C. Carrie Liu, MD, MPH
Assistant Professor, Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery
University of Arizona
Tucson
AZ
Disclosures
CCL declares she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
David E. Tunkel, MD
Professor of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
Director, Pediatric Otolaryngology
Johns Hopkins Children’s Center
Baltimore
MD
Disclosures
DT contributes to guidelines by the American Academy of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery.
Roderick P. Venekamp, MD, PhD
General Practitioner and Associate Professor of Primary Care
Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care
University Medical Center Utrecht
Utrecht University
The Netherlands
Disclosures
RPV declares he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Simon F, Haggard M, Rosenfeld RM, et al. International consensus (ICON) on management of otitis media with effusion in children. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2018 Feb;135(1s):S33-9.Full text Abstract
Rosenfeld RM, Shin JJ, Schwartz SR, et al. Clinical practice guideline: otitis media with effusion (update). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016 Feb;154(1 suppl):S1-41.Full text Abstract
Rosenfeld RM, Tunkel DE, Schwartz SR, et al. Clinical practice guideline: tympanostomy tubes in children (update). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022 Feb;166(1_suppl):S1-55.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Acute otitis media
- Myringitis
- Dilatory Eustachian tube dysfunction
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Clinical practice guideline: tympanostomy tubes in children (update)
- International consensus (ICON) on management of otitis media with effusion in children
More GuidelinesPatient information
Ear fluid after an infection
How to help your child avoid ear infections
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer