Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
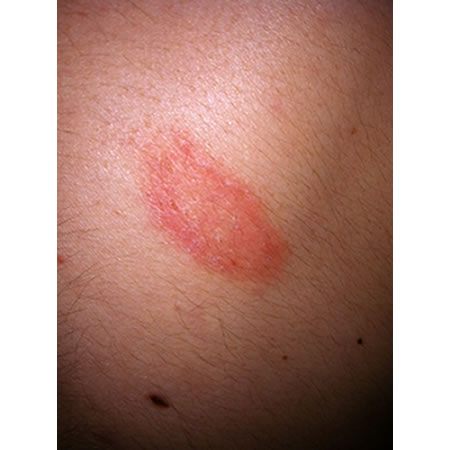
- herald patch
- pruritus
- age 10 to 35 years
- 2- to 12-week duration
- scale
- located on trunk and upper extremities
- fir-tree pattern distribution
- located on face, palms, soles, mucosa
- acute to subacute recurrent skin eruption
Other diagnostic factors
- 2-week timing between herald patch and new lesions
- female sex
- prodromal symptoms
- pigmentary alteration (severe cases/dark skin color)
Risk factors
- age 10 to 35 years
- female sex
Diagnostic tests
Tests to consider
- skin biopsy
- antistreptolysin O titers
- potassium hydroxide (KOH) prep microscopy or fungal culture
- rapid plasma reagin/Venereal Disease Research Laboratory
Treatment algorithm
mild to moderate symptoms
severe or refractory disease
refractory to all other treatments
Contributors
Authors
Daniela Kroshinsky, MD, MPH

Director of Inpatient Dermatology
Associate Professor of Dermatology
Massachusetts General Hospital
Harvard School of Medicine
Boston
MA
Disclosures
DK declares that she has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Dean S. Morrell would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Eve Lowenstein, Dr Ladan Shahabi, and Dr John English, previous reviewers of this topic.
Peer reviewers
Dean S. Morrell, MD
Clinical Professor
Department of Dermatology
University of North Carolina
Chapel Hill
NC
Disclosures
DSM declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Chuh A, Lee A, Zawar V, et al. Pityriasis rosea - an update. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2005 Sep-Oct;71(5):311-5.Full text Abstract
Chuh A, Zawar V, Lee A. Atypical presentations of pityriasis rosea: case presentations. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2005 Jan;19(1):120-6. Abstract
Contreras-Ruiz J, Peternel S, Jiménez Gutiérrez C, et al. Interventions for pityriasis rosea. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Oct 30;2019(10):CD005068.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.

Differentials
- Secondary syphilis
- Guttate psoriasis
- Tinea corporis
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Pityriasis rosea: diagnosis and treatment
- Pityriasis rosea: diagnosis and treatment
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer