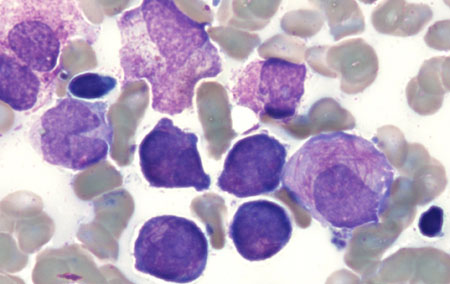
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- pallor
- ecchymoses or petechiae
Other diagnostic factors
- fatigue
- dizziness
- palpitations
- dyspnea
- fever and infections
- lymphadenopathy
- hepatosplenomegaly
- mucosal bleeding
- testicular mass
- skin mass (e.g., myeloid sarcoma)
- skin infiltration
- gingival enlargement
- bone pain
- gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., severe abdominal pain)
- neurologic symptoms (e.g., headache, confusion)
Risk factors
- age over 65 years
- previous treatment with chemotherapy
- previous hematologic disorders
- inherited genetic disorders
- constitutional chromosomal abnormalities
- ionizing radiation exposure
- benzene exposure
- environmental exposures
- male sex
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- CBC with differential
- peripheral blood smear
- coagulation panel
- serum electrolytes
- serum uric acid
- serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
- renal function
- liver function tests
- bone marrow evaluation
- genetic testing
Tests to consider
- genetic testing for heritable hematologic malignancy predisposition syndrome
- human leukocyte antigen (HLA) typing
- CNS imaging and lumbar puncture
- FDG-PET/CT scan
- chest x-ray
- echocardiogram
- multigated acquisition scan
- human leukocyte antigen (HLA) typing
Treatment algorithm
newly diagnosed AML: suitable for intensive chemotherapy
newly diagnosed AML: not suitable for intensive chemotherapy
newly diagnosed non-high-risk acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL)
newly diagnosed high-risk acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL)
complete remission: AML
complete remission: acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL)
relapsed or refractory AML
relapsed or refractory acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL)
Contributors
Authors
Vijaya Raj Bhatt, MBBS, MS
Associate Professor
Section Leader, Malignant Hematology
University of Nebraska Medical Center Division of Hematology-Oncology
Nebraska
NE
Disclosures
VRB has participated in a Safety Monitoring Committee for Protagonist Therapeutics. He serves as an Associate Editor for the Elsevier Journal, Current Problems in Cancer. He has received consulting fees from Imugene, Sanofi, and Taiho; research funding (institutional) from Abbvie, Pfizer, Incyte, Jazz, NMDP, MEI Pharma, Sanofi, and Actinium Pharmaceuticals; and drug support (institutional) from Chimerix for a trial.
Prajwal Dhakal, MBBS
Clinical Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine-Hematology, Oncology, and Blood and Marrow Transplantation
University of Iowa
Iowa City
IA
Disclosures
PD declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Vijaya Raj Bhatt and Dr Prajwal Dhakal would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Kavita Raj and Dr Priyanka Mehta, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
KR declares that she has no competing interests. PM is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Naveen Premnath, MD
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Division of Hematology, Oncology, and Transplantation
University of Minnesota
Minnesota
MN
Disclosures
NP declares that he has no competing interests.
Rebecca Connor, MD
Chief Fellow
Section of Hematology and Oncology
Department of Internal Medicine
Wake Forest University Baptist Medical Center
Winston-Salem
NC
Disclosures
RC declares that she has no competing interests.
Roger M. Lyons, MD, FACP
Clinical Professor of Medicine
University of Texas Health Science Center
San Antonio
Cancer Care Network of South Texas
San Antonio
TX
Disclosures
RML declares that he has no competing interests.
Shankaranarayana Paneesha, MD, MRCP, FRCPath
Consultant Haematologist
Department of Haematology and Stem Cell Transplantation
Heartlands Hospital
Birmingham
UK
Declarações
SP declares that he has no competing interests.
David Marks, MD, MRCP, MRCPath
Professor of Haematology & Stem Cell Transplantation
Department of Molecular and Cellular Medicine
University of Bristol
UK
Declarações
DM declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Döhner H, Wei AH, Appelbaum FR, et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood. 2022 Sep 22;140(12):1345-77.Texto completo Resumo
National Cancer Comprehensive Network. NCCN guidelines in oncology: acute myeloid leukemia [internet publication].Texto completo
Heuser M, Ofran Y, Boissel N, et al. Acute myeloid leukaemia in adult patients: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2020 Jun;31(6):697-712.Texto completo Resumo
Sanz MA, Fenaux P, Tallman MS, et al. Management of acute promyelocytic leukemia: updated recommendations from an expert panel of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood. 2019 Apr 11;133(15):1630-43.Texto completo Resumo
Sekeres MA, Guyatt G, Abel G, et al. American Society of Hematology 2020 guidelines for treating newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia in older adults. Blood Adv. 2020 Aug 11;4(15):3528-49.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
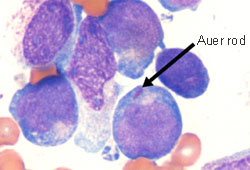
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
- Biphenotypic leukemia
- Myeloid/lymphoid neoplasms with eosinophilia and tyrosine kinase fusion genes (MLNE)
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- NCCN guidelines in oncology: acute myeloid leukemia
- NCCN practice guidelines in oncology: hematopoietic cell transplantation
Mais DiretrizesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal