Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- blood pressure (BP) >180/120 mmHg
Other diagnostic factors
- neurologic symptoms
- cardiac symptoms
- abnormal cardiopulmonary exam
- abnormal abdominal exam
- oliguria or polyuria
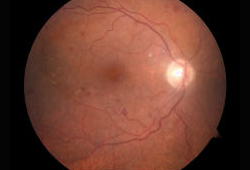
- abnormal fundoscopic exam
- abnormal neurologic exam
Risk factors
- inadequately treated hypertension
- chronic kidney disease
- renal artery stenosis
- renal transplant
- endocrine disorders with known hypertensive effects
- pregnancy
- older age
- black ethnicity
- male sex
- use of sympathomimetic drugs
- pharmacotherapy with known hypertensive effect
- obstructive sleep apnea
- vasculitis and connective tissue diseases
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- blood chemistry
- CBC with smear
- urinalysis with microscopy
- ECG
- chest x-ray
Tests to avoid
- plasma catecholamines
Tests to consider
- thyroid function tests
- liver function tests
- cardiac enzymes
- N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP)
- coagulation profile
- urine or serum pregnancy test
- urine toxicology screen
- computed tomography angiography (CTA) scan
- transthoracic echocardiography (TTE)
- renal ultrasound with Doppler
- head CT without contrast
- head MRI
- plasma renin activity and aldosterone level
- spot urine or plasma metanephrine
- 24-hour urine free cortisol
- sleep study
Treatment algorithm
accelerated (malignant) hypertension or hypertensive encephalopathy or intracranial hemorrhage
acute ischemic stroke
myocardial ischemia/infarction
left ventricular failure and/or pulmonary edema
aortic dissection
acute kidney injury
hyperadrenergic state
severe hypertension in pregnancy (preeclampsia and eclampsia)
Contributors
Authors
M. Lee Sanders, PhD, MD
Clinical Associate Professor
Division of Nephrology
University of Iowa
Iowa City
IA
Disclosures
MLS is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Manish Suneja, MD, FASN, FACP
Clinical Professor
Division of Nephrology
University of Iowa
Iowa City
IA
Disclosures
MS receives royalties from McGraw Hill as the editor of DeGowin’s Diagnostic Examination and is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Acknowledgements
Dr M. Lee Sanders and Dr Manish Suneja would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Hector Ventura and Dr Madhavi T. Reddy, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
HV declares that he has no competing interests. MTR is employed by Merck and owns stocks in Merck, and Johnson & Johnson.
Peer reviewers
Aparna Sundaram, DO, MBA, MPH
Physician Consultant
Preventive Medicine
Private Practice
Atlanta
GA
Disclosures
AS declares that she has no competing interests.
Ethan Cumbler, MD
Assistant Professor
Department of Internal Medicine
University of Colorado Health Sciences Center
Denver
CO
Disclosures
EC declares that he has no competing interests.
Michael Schachter, MB, BSc, FRCP
Department of Clinical Pharmacology
St Mary’s Hospital
Imperial College
London
UK
Disclosures
MS declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 May 15;71(19):e127-248.Full text Abstract
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice bulletin no. 222: gestational hypertension and preeclampsia. Jun 2020 [internet publication].Full text Abstract
Mancia G, Kreutz R, Brunström M, et al. 2023 ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension: endorsed by the International Society of Hypertension (ISH) and the European Renal Association (ERA). J Hypertens. 2023;41(12):1874-2071.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Hypertensive urgency
- Uncontrolled essential hypertension
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- The management of elevated blood pressure in the acute care setting
- Hypertension in adults: diagnosis and management
More GuidelinesPatient information
High blood pressure
High blood pressure: what is it?
More Patient informationVideos
Venepuncture and phlebotomy: animated demonstration
How to perform an ECG: animated demonstration
More videosLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer