Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
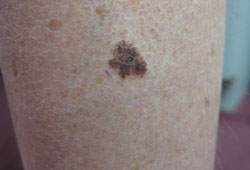
- altered pigmented lesion (ABCDE signs)
- melanocytic lesion that does not resemble surrounding melanocytic nevi ("ugly duckling")
- spontaneous bleeding or ulceration of a pigmented lesion
- constitutional symptoms
- nail sign: persistent single-nail melanonychia striata
- nail sign: Hutchinson sign
- atypical dermoscopy findings
- fixed lymphadenopathy
- in-transit metastases
Risk factors
- sun exposure
- family history of melanoma
- personal history of melanoma
- personal history of skin cancer (including actinic damage)
- history of atypical nevi
- Fitzpatrick skin type I or II (white skin)
- red or blond hair color
- high freckle density
- sun bed use
- light eye color
- increased numbers of benign-appearing melanocytic nevi
- large congenital nevi
- immunosuppression
- xeroderma pigmentosum
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- dermoscopy
- skin biopsy
- immunohistochemistry
Tests to consider
- ultrasound
- sentinel lymph node biopsy
- chest/abdominal/pelvic CT scan
- whole-body PET scan
- brain imaging (CT or MRI)
- BRAF mutational analysis
- NRAS mutational analysis
- serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
Emerging tests
- CDKN2A mutational analysis
Treatment algorithm
early stage melanoma (melanoma in situ, stage I, stage II)
stage III melanoma with negative sentinel nodes
stage III melanoma with positive sentinel nodes
stage III melanoma with clinically positive nodes: resectable
stage III melanoma with satellite/in-transit metastases: limited resectable disease
stage III melanoma with satellite/in-transit metastases: borderline resectable or unresectable disease
stage IV metastatic melanoma
Contributors
Authors
Alvin J. X. Lee, PhD, FRCP
Consultant Medical Oncologist
Department of Medical Oncology
Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust
London
UK
Disclosures
AJXL declares that he has no competing interests.
Yin Wu, MRCP(UK), PhD
Wellcome Trust Career Development Fellow and Honorary Consultant Medical Oncologist
Centre for Inflammation Biology and Cancer Immunology
King's College London
Department of Medical Oncology
Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust
London
UK
Disclosures
YW is funded by the Wellcome Trust. YW consults for E15 VC and Boxer Capital, and has held advisory roles for Bristol Meyers Squibb and Sun Pharma.
Amanda Fitzpatrick, MRCP(UK), PhD
Medical Oncologist and Honorary Senior Lecturer
Guy's Cancer Centre
King's College
London
UK
Disclosures
AF has received research funding from Gilead Sciences and Daiichi Sankyo.
Pablo Fernandez-Peñas, MD, PhD, FACD
Professor of Dermatology
The University of Sydney
Sydney
Australia
Declarações
PFP declares that he has no competing interests with the topic Melanoma. PFP has served on advisory boards for AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Johnson & Johnson, L’Oreal, LEO Pharma, Merck, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB; has given educational lectures for AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, L’Oreal, LEO Pharma, Merck, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, UCB Pharma and Zuellig Pharma; has received research funding from Pfizer; has conducted clinical trials for AbbVie, Akesobio, Alumis, Amgen, Apogee, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, CellDex, CSL, Chugai, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Galderma, Incyte, Johnson & Johnson, Jiangsu Hengrui, KoBioLabs, Merck, Merck Sharp & Dohme, miRagen, Moderna, Nektar, Novartis, OncoSec, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, UCB Pharma.
Agradecimentos
Dr Alvin J. X. Lee, Dr Yin Wu, Dr Amanda Fitzpatrick, and Dr Pablo Fernandez-Peñas would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Prachi Bhave, Dr Robyn P.M. Saw, Dr Sophie E. Papa, Dr Alexander M. Menzies, Dr Philip Friedlander, Dr Hobart W. Walling, and Dr Brian L. Swick, previous contributors to this topic.
Declarações
PB has received honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD and Novartis and sponsorship from MSD and Novartis. RPMS is on the advisory board for Novartis, MSD, and Qbiotics and has previously been on the advisory board for Amgen; he has received honoraria from BMS and Novartis. SEP has received honoraria from BMS, MSD, and Novartis to attend conferences; she has participated in advisory boards for BMS, MSD, Amgen, Roche, and GSK. AMM has received honoraria from Novartis and BMS; he is on the advisory boards of MSD and Chugai. PF is a consultant for Genentech. HWW and BLS declare that they have no competing interests.
Revisores
David Cassarino, MD, PhD
Assistant Professor
Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
University of California
Los Angeles
CA
Declarações
DC declares that he has no competing interests.
James DeBloom, MD
Dermatologist/Dermatologic Surgeon
President of the South Carolina Skin Cancer Center
Greenville
SC
Declarações
JB declares that he has no competing interests.
Mai Brooks, MD, FACS
Associate Director
JCCC Women's Cancers Program Area
Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center at UCLA
Los Angeles
CA
Declarações
MB declares that she has no competing interests.
Karol Sikora, MA, MBBCh, PhD, FRCR, FRCP, FFPM
Medical Director
CancerPartnersUK
London
UK
Declarações
KS declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: melanoma - cutaneous [internet publication].Texto completo
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Melanoma: assessment and management. Jul 2022 [internet publication].Texto completo
Amaral T, Ottaviano M, Arance A, et al. Cutaneous melanoma: ESMO clinical practice guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2025 Jan;36(1):10-30.Texto completo Resumo
Seth R, Agarwala SS, Messersmith H, et al. Systemic therapy for melanoma: ASCO guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2023 Oct 20;41(30):4794-820.Texto completo Resumo
Vogelbaum MA, Brown PD, Messersmith H, et al. Treatment for brain metastases: ASCO-SNO-ASTRO guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2022 Feb 10;40(5):492-516.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Benign/dysplastic melanocytic nevi
- Seborrheic keratosis
- Pigmented basal cell carcinoma
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Suspected cancer: recognition and referral
- European consensus-based interdisciplinary guideline for melanoma. Part 2: treatment
Mais DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Skin cancer (melanoma): what is it?
Skin cancer (melanoma): how is it diagnosed and treated?
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal