Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- polyuria
- polydipsia
- diabetic ketoacidosis
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- young age
- weight loss
- blurred vision
- nausea and vomiting
- abdominal pain
- tachypnea
- clinical dehydration
- lethargy
- altered mental status
Fatores de risco
- genetic predisposition
- geographic region
- infectious agents
- dietary factors
- use of immunotherapy
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- HbA1c
- fasting plasma glucose
- 2-hour post-glucose load plasma glucose
- random plasma glucose
Investigações a serem consideradas
- plasma or urine ketones
- random C-peptide
- autoimmune markers
Algoritmo de tratamento
nonpregnant
pregnant
Colaboradores
Autores
Rajesh K. Garg, MD

Professor of Medicine
David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
Harbor-UCLA Medical Center
Torrance
CA
Declarações
RKG is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Agradecimentos
Dr Rajesh K. Garg would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Varsha Vimalananda, previous contributor to this topic.
Declarações
VV declares that she has no competing interests.
Revisores
Zachary Bloomgarden, MD
Clinical Professor
Medicine/Endocrinology
Diabetes and Bone Disease
Mount Sinai School of Medicine
New York
NY
Declarações
ZB declares that he has no competing interests.
Alicia Jenkins, MB, BS, MD, FRACP, FRCP
Associate Professor
Department of Medicine
University of Melbourne
Melbourne
Australia
Professor
Harold Hamm Oklahoma Diabetes Center
University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center
Oklahoma City
OK
Declarações
AJ has been a (non-salaried) co-investigator on multi-center clinical trials supported by Novo, Eli Lilly, Sanofi-Aventis, and Medtronic. She does not hold any stocks or shares in these companies. She has received a speaker's honorarium from Novo Nordisk.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
American Diabetes Association. Standards of care in diabetes - 2025. Diabetes Care. 2025 Jan;48(1):S344-52.Texto completo
Norris JM, Johnson RK, Stene LC. Type 1 diabetes-early life origins and changing epidemiology. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020 Mar;8(3):226-38.Texto completo Resumo
International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes. ISPAD clinical practice consensus guidelines 2024. Dec 2024 [nternet publication].Texto completo
Holt RIG, DeVries JH, Hess-Fischl A, et al. The management of type 1 diabetes in adults. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia. 2021 Dec;64(12):2609-52.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
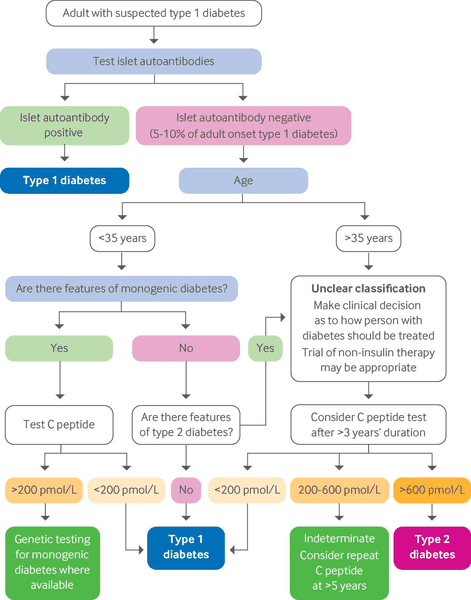
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Monogenic diabetes: maturity onset diabetes of the young
- Monogenic diabetes: neonatal diabetes mellitus
- Type 2 diabetes
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Standards of care in diabetes - 2025
- Management of individuals with diabetes at high risk for hypoglycemia
Mais DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Diabetes type 1: what is it?
Diabetes type 1: what are the treatment options?
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal