Nipocalimab approved by FDA for treatment of generalized myasthenia gravis
Nipocalimab, a neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) antagonist monoclonal antibody, has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of generalized myasthenia gravis in adults and children ≥12 years who are positive for acetylcholine receptor (AChR) or muscle-specific tyrosine kinase (MuSK) antibodies. The approval follows FDA priority review designation and provides an alternative treatment option to offer sustained disease control for a broad range of patients with troublesome symptoms caused by myasthenia gravis.
The approval was based on results from Vivacity-MG3, a phase 3 trial of patients with generalized myasthenia gravis inadequately controlled with standard therapy. Nipocalimab added to standard care was associated with long-lasting reductions in total circulating IgG and AChR antibodies, and improvements in patient-reported outcomes, with a good safety profile.
Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
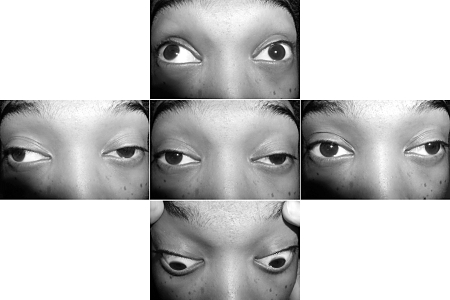
- muscle strength fatigability
- ptosis
- diplopia
- dysphagia
- dysarthria
- facial paresis
- proximal limb weakness
- shortness of breath
Fatores de risco
- family history of autoimmune disorders
- genetic markers
- cancer-targeted therapy
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- serum acetylcholine receptor (AChR) antibody analysis
- muscle-specific tyrosine kinase (MuSK) antibodies
- serial pulmonary function tests
Investigações a serem consideradas
- striational receptor antibody assays
- repetitive nerve stimulation
- single-fiber EMG
- CT of chest
Algoritmo de tratamento
myasthenic crisis
mild to moderate disease (class I to III)
severe (class IV or V) or refractory disease
Colaboradores
Autores
David P. Richman, MD
Distinguished Professor
Professor of Neurology
University of California - Davis
Davis
CA
Declarações
DPR declares that he has no competing interests.
Agradecimentos
Dr David Richman would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Robert Lisak, Dr Andrea Corse, and Dr Ami Mankodi, previous contributors to this topic.
Declarações
AC and AM declare that they have no competing interests. RPL is a Data and Safety Monitoring Board Member for the COUR myasthenia gravis clinical trial. RPL is a site principal investigator for clinical trials and a co-author for the clinical trial reports for myasthenia gravis therapies for Alexion, Argenx, and UCB Ra. RPL's institution receives payment for the time spent on these clinical trials. RPL has received book royalties from Oxford University Press and Blackstone, and has carried out consultancy work for Avilar.
Revisores
Vern C. Juel, MD
Associate Professor of Medicine (Neurology)
Duke University
Durham
NC
Declarações
VCJ declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Narayanaswami P, Sanders DB, Wolfe G, et al. International consensus guidance for management of myasthenia gravis: 2020 update. Neurology. 2021 Jan 19;96(3):114-22.Texto completo Resumo
Skeie GO, Apostolski S, Evoli A, et al. Guidelines for treatment of autoimmune neuromuscular transmission disorders. Eur J Neurol. 2010 Jul;17(7):893-902.Texto completo Resumo
Gronseth GS, Barohn R, Narayanaswami P. Practice advisory: thymectomy for myasthenia gravis (practice parameter update). Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 2020 Apr 21;94(16):705-9.Texto completo Resumo
Elovaara I, Apostolski S, van Doorn P, et al. EFNS guidelines for the use of intravenous immunoglobulin in treatment of neurological diseases: EFNS task force on the use of intravenous immunoglobulin in treatment of neurological diseases. Eur J Neurol. 2008 Sep;15(9):893-908.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS)
- Botulism
- Penicillamine-induced myasthenia gravis
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- International consensus guidance for management of myasthenia gravis: 2020 update
- Practice advisory: thymectomy for myasthenia gravis (practice parameter update)
Mais DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Myasthenia gravis
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesVideos
Venepuncture and phlebotomy: animated demonstration
Peripheral intravascular catheter: animated demonstration
Mais vídeosConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal