Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- antecedent tetanus-prone injury
- tetanus immunization status
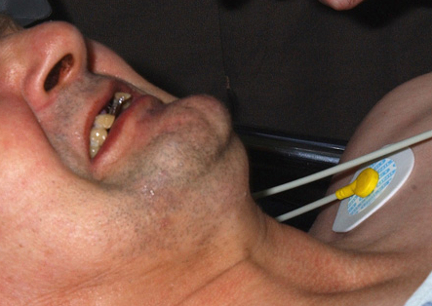
- trismus (lock jaw)
- back pain
- muscle stiffness/increased tone
- dysphagia
- spasms
Other diagnostic factors
- people who inject drugs
- respiratory distress
- labile blood pressure, pulse rate, and temperature
- sweating
Risk factors
- incomplete tetanus immunization
- injury
- aseptic obstetric practices
- people who inject drugs
- asterile intramuscular injection
- abdominal surgery
- acupuncture, ear piercing, pedicures, toothpicks
- necrotic tumors
- middle ear infection
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- clinical diagnosis
Tests to consider
- serum toxin
- Clostridium tetani detection from wound tissue or swab
- serum antitoxin antibodies
- spores on drug samples or paraphernalia
- lumbar puncture
- electroencephalogram
- electromyogram
Treatment algorithm
clean and minor wound
tetanus-prone wound
with clinical tetanus
Contributors
Authors
Russell W. Steele, MD
Clinical Professor of Pediatrics
Tulane University School of Medicine
New Orleans
LA
Disclosures
RWS declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Russell W. Steele would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Christopher M. Parry, Dr Nicholas J. Beeching, Dr Lucy E. Cottle, and Professor Enitan D. Carrol, the previous contributors to this topic.
Peer reviewers
Louise Thwaites, BSc, MBBS, MD
Senior Clinical Research Fellow
Oxford University Clinical Research Unit
Hospital for Tropical Diseases
Ho Chi Minh City
Vietnam
Centre for Tropical Medicine and Global Health
Oxford University
Oxford, UK
Disclosures
LT is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Katrina Kretsinger, MD, MA
Commander
U.S. Public Health Service
Medical Epidemiologist
HIV Vaccine Team
Epidemiology Branch
Division of HIV/AIDS Prevention
National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Atlanta, GA
Disclosures
KK declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
UK Health Security Agency. Tetanus: the green book, chapter 30. Jun 2022 [internet publication].Full text
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Child and adolescent immunization schedule by age: recommendations for ages 18 years or younger, United States, 2025. Nov 2024 [internet publication].Full text
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Adult immunization schedule by age: recommendations for ages 19 years or older, United States, 2025. Nov 2024 [internet publication].Full text
Havers FP, Moro PL, Hunter P, et al. Use of tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid, and acellular pertussis vaccines: updated recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices - United States, 2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020 Jan 24;69(3):77-83.Full text Abstract
Tiwari TSP, Moro PL, Acosta AM. Tetanus. In: Hall E, Wodi AP, Hamborsky J, et al, eds. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Epidemiology and vaccine-preventable diseases. 14th ed. Washington, D.C.: Public Health Foundation; 2021.Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Drug-induced dystonias, for example, phenothiazines
- Strychnine poisoning
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Child and adolescent immunization schedule by age: recommendations for ages 18 years or younger, United States, 2025
- Adult immunization schedule by age: recommendations for ages 19 years or older, United States, 2025
More GuidelinesPatient information
DTaP vaccine (diphtheria, tetanus, polio, and pertussis)
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer