Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- cardiac disease
Other diagnostic factors
- medications
- palpitations
- fatigue, weakness
- chest pain
- shortness of breath, cough
- nausea, vomiting
- lightheadedness, syncope
- rales
- edema
Risk factors
- substance misuse (alcohol ingestion/withdrawal, cocaine, amphetamines)
- digoxin toxicity
- previous cardiac surgery to correct congenital heart defects
- coronary artery disease
- exacerbation of chronic lung disease
- theophylline
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- ECG
- digoxin level
- theophylline level
- CXR
- electrolytes
- toxicology screen
Tests to consider
- vagal maneuvers, adenosine
- thyroid-stimulating hormone
- echocardiogram
- ambulatory 24-hour (Holter) ECG or event recorder
- electrophysiologic study (EPS)
Treatment algorithm
adult: undifferentiated supraventricular tachycardia
adult: focal AT; digoxin excess not suspected
adult: focal AT; digoxin toxicity suspected
child
adult: sustained or recurrent focal AT
Contributors
Authors
Danesh Kella, MBBS, FHRS
Assistant Professor
Department of Cardiovascular Diseases
Division of Heart Rhythm
Mayo Clinic
Jacksonville
FL
Disclosures
DK receives honoraria from Zoll Medical.
Acknowledgements
Dr Danesh Kella would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Sarah Stahmer, previous contributor to this topic.
Peer reviewers
Kathryn L. Berlacher, MD, MS
Assistant Professor and Cardiology Fellowship Program Director
University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
Pittsburgh
PA
Declarações
KLB declares that she has no competing interests.
Mehak Dhande, MD
Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Fellow
University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
Pittsburgh
PA
Declarações
MD declares that she has no competing interests.
Amal Mattu, MD
Associate Professor of Emergency Medicine
University of Maryland Medical Center
Baltimore
MD
Declarações
AM declares that he has no competing interests.
Vias Markides, MB(Hons), BS(Hons), MD, FRCP
Consultant Cardiologist
Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Trust
Imperial College London
London
UK
Declarações
VM declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Page RL, Joglar JA, Caldwell MA, et al. 2015 ACC/AHA/HRS guideline for the management of adult patients with supraventricular tachycardia: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016 Apr 5;67(13):e27-e115.Texto completo Resumo
Brugada J, Katritsis DG, Arbelo E, et al. 2019 ESC guidelines for the management of patients with supraventricular tachycardia. The Task Force for the management of patients with supraventricular tachycardia of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2020 Feb 1;41(5):655-720.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
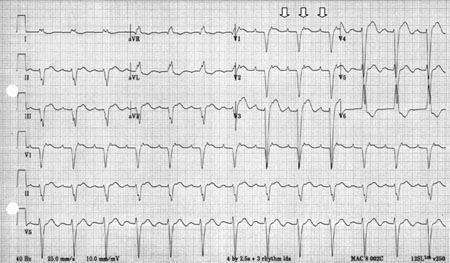
Differentials
- Sinus tachycardia
- AV node re-entrant tachycardia
- AV re-entrant tachycardia or accessory pathway mediated tachycardia
Mais DifferentialsGuidelines
- JCS/JHRS 2020 guideline on pharmacotherapy of cardiac arrhythmias
- 2019 ESC guidelines for the management of patients with supraventricular tachycardia
Mais GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer