Resumo
Definição
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- anemia
- bone pain
- monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS)
Other diagnostic factors
- hypercalcemia
- infections
- fatigue
- renal impairment
Risk factors
- monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS)
- abnormal free light-chain ratio
- male sex
- black ethnicity
- family history of MM
- radiation exposure
- petroleum products exposure
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- serum quantitative immunoglobulins
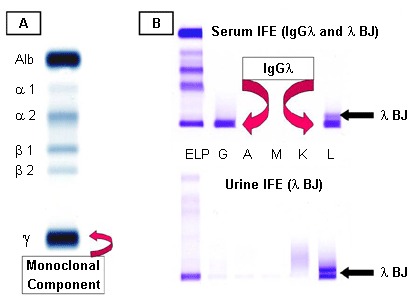
- serum/urine protein electrophoresis
- serum/urine immunofixation
- serum free light-chain assay
- whole-body low-dose CT (WBLD-CT)
- whole-body 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography/CT (FDG-PET/CT)
- bone marrow evaluation
- serum calcium
- CBC with differential
- peripheral blood smear
- serum creatinine, BUN, electrolytes
- serum uric acid
- liver function tests
- C-reactive protein (CRP)
- serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
- serum beta2-microglobulin
- serum albumin
- N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) or BNP
Investigations to consider
- whole-body MRI
- skeletal survey
- cytogenetic analysis
- mass spectrometry
- genetic testing
- serum viscosity
- viral infection screening
- clonotype identification
- renal biopsy
Treatment algorithm
newly diagnosed transplant candidates
newly diagnosed nontransplant candidates
patients responding to initial treatment
relapsing or refractory disease
Contributors
Authors
Matthew M. Lei, PharmD
Clinical Pharmacist Medical Oncology
Massachusetts General Hospital
Boston
MA
Disclosures
MML has received honoraria for consultancy and speaker fees from Genentech and MJH Life Sciences, and for consultancy from Genmab, Astra Zeneca, CX4D, SERB Pharmaceuticals, and Sanofi. MML is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Diana Cirstea, MD
Medical Oncologist
Center for Multiple Myeloma
Massachusetts General Hospital
Harvard Medical School
Boston
MA
Disclosures
DC is on the advisory board for Sanofi.
E. Bridget Kim, PharmD, BCPS, BCOP
Clinical Pharmacist
Massachusetts General Hospital
Boston
MA
Disclosures
EBK declares that she has no competing interests.
Noopur Raje, MD

Director of Multiple Myeloma Program
Massachusetts General Hospital
Harvard Medical School
Boston
MA
Disclosures
NR has served on steering committees for Amgen and Roche; has held membership on an entity's boards of directors or advisory committees for Novartis, Takeda Pharmaceuticals USA Inc, Merck, Celgene, Onyx Pharmaceuticals, Immuneel Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen Biotech, Caribou Biosciences, and Bluebirdbio; and has received research funding from Bluebirdbio. NR is an author of several references cited in this topic.
Acknowledgements
Dr Matthew M. Lei, Dr Diana Cirstea, Dr E. Bridget Kim, and Dr Noopur Raje would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Loredana Santo and Dr Sonia Vallet, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
LS and SV declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Shaji Kumar, MD
Associate Professor of Medicine
Mayo Clinic
Rochester
MN
Disclosures
SK declares that he has no competing interests.
Faith Davies, MD
Institute of Cancer Research
Sutton
Surrey
UK
Disclosures
FD declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Rajkumar SV, Dimopoulos MA, Palumbo A, et al. International Myeloma Working Group updated criteria for the diagnosis of multiple myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2014 Nov;15(12):e538-48.Full text Abstract
Dimopoulos MA, Moreau P, Terpos E, et al. Multiple myeloma: EHA-ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. Ann Oncol. 2021 Mar;32(3):309-22.Full text Abstract
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: multiple myeloma [internet publication].Full text
Sive J, Cuthill K, Hunter H, et al. Guidelines on the diagnosis, investigation and initial treatment of myeloma: a British Society for Haematology/UK Myeloma Forum Guideline. Br J Haematol. 2021 Apr;193(2):245-68.Full text Abstract
Mikhael J, Ismaila N, Cheung MC, et al. Treatment of multiple myeloma: ASCO and CCO joint clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2019 May 10;37(14):1228-63.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.

Differentials
- Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance
- Solitary plasmacytoma
- Waldenström macroglobulinemia
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: multiple myeloma
- NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: hematopoietic cell transplantation
More GuidelinesPatient information
Multiple myeloma
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer