Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- chest pain
- diaphoresis
- cardiogenic shock
- acute heart failure
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- nausea and vomiting
- epigastric pain
- arrhythmias
- abnormal heart sounds
- shortness of breath
- syncope
- early morning onset
Fatores de risco
- smoking
- hypertension
- diabetes
- obesity and metabolic syndrome phenotype
- sedentary behavior and physical inactivity
- dyslipidemia
- chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- atherosclerosis (history of angina, myocardial infarction, stroke, transient ischemic attack, peripheral vascular disease)
- family history of premature coronary artery disease (CAD)
- age >60 years
- cocaine use
- depression
- stent thrombosis or restenosis
- sleep apnea
- surgical procedures (including intraoperative and postoperative periods)
- migraine
- adverse pregnancy outcomes
- anticholinergic burden
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- ECG
- cardiac biomarkers
- echocardiography
- CXR
- CBC
- BUN and serum creatinine
- electrolytes
- LFTs
- blood glucose
- CRP
Tests to avoid
- coronary artery calcium (CAC)
Investigações a serem consideradas
- angiography/cardiac catheterization
- lipids
- brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) or N-terminal pro-BNP (NT-pro-BNP)
- stress testing
- coronary CT angiography (CCTA)
Algoritmo de tratamento
acute presentation
post-stabilization
Colaboradores
Consultores especialistas
Mahi L. Ashwath, MD, MBA, FACC, FASE, FSCMR
Professor of Medicine and Radiology
Multimodality Imaging Director
Inaugural Reuben Jacobs Chair in Internal Medicine
UHS/UT Heart and Vascular Institute
San Antonio
TX
Declarações
MLA declares that she is a consultant for Tersera.
Agradecimentos
Dr Mahi L. Ashwath would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Sanjay Gandhi, Dr Cody Deen, Dr Sripal Bangalore, Dr Mina Owlia, Dr Thomas Vanhecke, and Dr Dena Krishnan, the previous contributors to this topic.
Declarações
SG declares that he is Senior Director of Medical Strategy and Innovation for the US market at Philips. SG is a senior advisor at Emeritus. SG is a voluntary board member of the American College of Cardiology (ACC) National Cardiovascular Data Registry oversight committee, the Chest Pain Myocardial Infarction registry steering committee, and the ACC finance committee. CSD was previously the Director of Cardiac Rehab for Chatham Hospital, which was financially set up as a consultancy relationship, until 2017. CSD has spoken (unpaid) at the Update in Cardiology and Update in Internal Medicine Conferences at UNC for the last 5 years. CSD has served as the PI for the Dal-GeneE (site now closed) and the ACCELERATE Trials at the University of North Carolina (trial now completed). Each trial required paid travel to an investigator meeting. SB, MO, TV, and DK declare that they have no competing interests.
Revisores
Syed Wamique Yusuf, MBBS, FRCPI
Professor of Medicine
Department of Cardiology
University of Texas
MD Anderson Cancer Center
Houston
TX
Declarações
SWY declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Rao SV, O'Donoghue ML, Ruel M, et al. 2025 ACC/AHA/ACEP/NAEMSP/SCAI guideline for the management of patients with acute coronary syndromes: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2025 Apr;151(13):e771-862.Texto completo Resumo
Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al; Executive Group on behalf of the Joint European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA)/World Heart Federation (WHF) Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Oct 30;72(18):2231-64.Texto completo Resumo
Byrne RA, Rossello X, Coughlan JJ, et al. 2023 ESC guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J. 2023 Oct 12;44(38):3720-826.Texto completo
Writing Committee Members; Gulati M, Levy PD, Mukherjee D, et al. 2021 AHA/ACC/ASE/CHEST/SAEM/SCCT/SCMR guideline for the evaluation and diagnosis of chest pain: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee On Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021 Nov 30;78(22):e187-285.Texto completo Resumo
Amsterdam EA, Wenger NK, Brindis RG, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014 Dec 23;64(24):e139-228.Texto completo Resumo
Lawton JS, Tamis-Holland JE, Bangalore S, et al. 2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI guideline for coronary artery revascularization: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee On Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Jan 18;145(3):e18-114.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
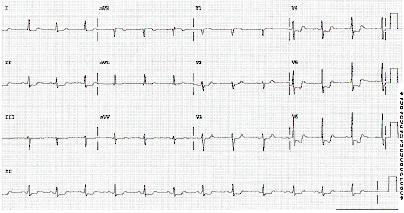
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)
- Unstable angina
- Aortic dissection
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- 2025 ACC/AHA/ACEP/NAEMSP/SCAI guideline for the management of patients with acute coronary syndromes: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on clinical practice guidelines
- 2025 ACC/AHA/ACEP/NAEMSP/SCAI guideline for the management of patients with acute coronary syndromes
Mais DiretrizesCalculadoras
ASCVD Risk Estimator Plus
ASCVD Risk Estimator Plus
Mais CalculadorasFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Heart attack
Heart attack: what is it?
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal