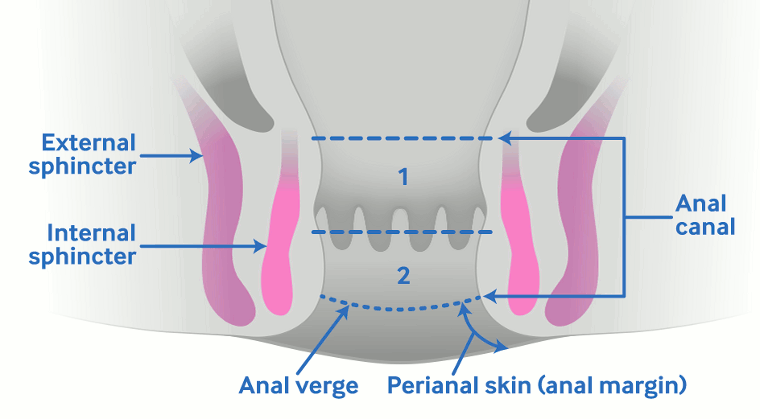
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- rectal bleeding
- rectal pain
- rectal mass
Other diagnostic factors
- anal discharge
- anal itching
- fecal incontinence
- anal fistula
- nonhealing ulcer
- inguinal node mass
- features of distant metastasis
Risk factors
- HPV
- HIV
- immunosuppression
- receptive anal intercourse
- multiple sexual partners
- autoimmune disease
- smoking
- anal intraepithelial neoplasia
- anal fistula
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- anoscopy
- biopsy of tumor
- pelvis MRI scan
- pelvis CT scan
- abdominal and chest CT scan
Tests to consider
- PET scan
- inguinal node needle biopsy
- serum HIV enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- cervical cancer screening
Treatment algorithm
locoregional disease
distant metastatic disease
Contributors
Authors
Bruce D. Minsky, MD
Professor and Frank T. McGraw Endowed Chair
Radiation Oncology
MD Anderson Cancer Center
Houston
TX
Disclosures
BDM declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Brian Czito, MD
Associate Professor
Department of Radiation Oncology
Duke University Medical Center
Durham
NC
Disclosures
BC declares that he has no competing interests.
Lisa Kachnic, MD
Chief and Associate Professor
Department of Radiation Oncology
Boston University Medical Center
Boston
MA
Disclosures
LK has received funding from the US Department of Defense to perform research on non-anal cancers. LK is the author of a study referenced in this topic.
Sue Clark, MD
Consultant Colorectal Surgeon
Assistant Director
The Polyposis Registry
St Mark's Hospital
Harrow
UK
Disclosures
SC declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Rao S, Guren MG, Khan K, et al. Anal cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2021 Sep;32(9):1087-100.Full text Abstract
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: anal carcinoma [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Hemorrhoids
- Rectal cancer
- Anal margin cancer
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: management of immune checkpoint inhibitor-related toxicities
- Radiation therapy for anal squamous cell carcinoma
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer