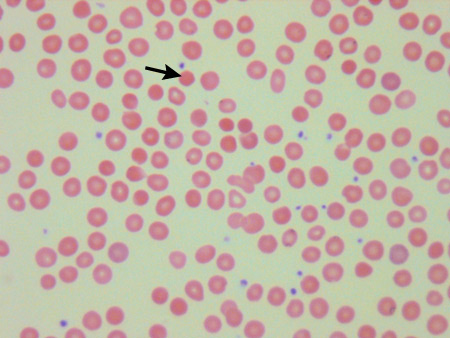
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- positive family history
- at risk demographic
- pallor
- jaundice
- splenomegaly
Other diagnostic factors
- fatigue
- hydrops fetalis or stillbirth
Risk factors
- family history of splenectomy, anemia, jaundice, or hereditary spherocytosis (HS)
- at risk demographic
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- CBC
- reticulocyte count
- blood smear
- serum bilirubin
- serum aminotransferases
- direct antiglobulin test (DAT)
Tests to consider
- eosin-5-maleimide binding test
- acidified glycerol lysis test
- cryohemolysis test
- genetic analysis
- sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
Treatment algorithm
neonates (<28 days old)
infants (>28 days old), children, and adults: severe hereditary spherocytosis (HS)
infants (>28 days old), children, and adults: mild-to-moderate hereditary spherocytosis (HS)
Contributors
Authors
Shelley Crary, MD, MSCS
Associate Professor of Pediatrics
University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
Little Rock
AR
Disclosures
SC is reimbursed for membership on a drug and safety monitoring board (Novartis) for a nonrelated drug.
Acknowledgements
Dr Shelley Crary would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Paula Bolton-Maggs, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
PB-M has received travel and accommodation payments to give a series of lectures on pediatric hematology, one of which was on HS. She also was an expert witness in a legal case concerning a child with HS. PB-M is an author of some references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Robert Schilling, MD
Professor of Medicine Emeritus
School of Medicine and Public Health
University of Wisconsin-Madison
Madison
WI
Disclosures
RS is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Eber SW, Armbrust R, Schroter W. Variable clinical severity of hereditary spherocytosis: relation to erythrocytic spectrin concentration, osmotic fragility, and autohemolysis. J Pediatr. 1990 Sep;117(3):409-16. Abstract
Bolton-Maggs PH, Langer JC, Iolascon A, et al; General Haematology Task Force of the British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of hereditary spherocytosis - 2011 update. Br J Haematol. 2012 Jan;156(1):37-49.Full text Abstract
Perrotta S, Gallagher PG, Mohandas N. Hereditary spherocytosis. Lancet. 2008 Oct 18;372(9647):1411-26. Abstract
King MJ, Garçon L, Hoyer JD, et al. ICSH guidelines for the laboratory diagnosis of nonimmune hereditary red cell membrane disorders. Int J Lab Hematol. 2015 Jun;37(3):304-25.Full text Abstract
Iolascon A, Andolfo I, Barcellini W, et al. Recommendations regarding splenectomy in hereditary hemolytic anemias. Haematologica. 2017 Aug;102(8):1304-13.Full text Abstract
Davies JM, Lewis MP, Wimperis J, et al. Review of guidelines for the prevention and treatment of infection in patients with an absent or dysfunctional spleen: prepared on behalf of the British Committee for Standards in Haematology by a working party of the Haemato-Oncology task force. Br J Haematol. 2011 Nov;155(3):308-17.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
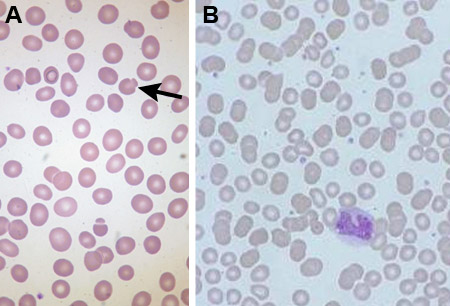
Differentials
- Nonhemolytic anemia
- Other causes of hemolytic anemia
- Other causes of spherocytosis
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Recommendations regarding splenectomy in hereditary hemolytic anemias
- ICSH guidelines for the laboratory diagnosis of non-immune hereditary red cell membrane disorders
More GuidelinesPatient information
Jaundice in newborn babies
Gallstones
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer